Enhancing Data Security in Healthcare IoT: An Innovative Blockchain-based Solution
Main Article Content
Abstract
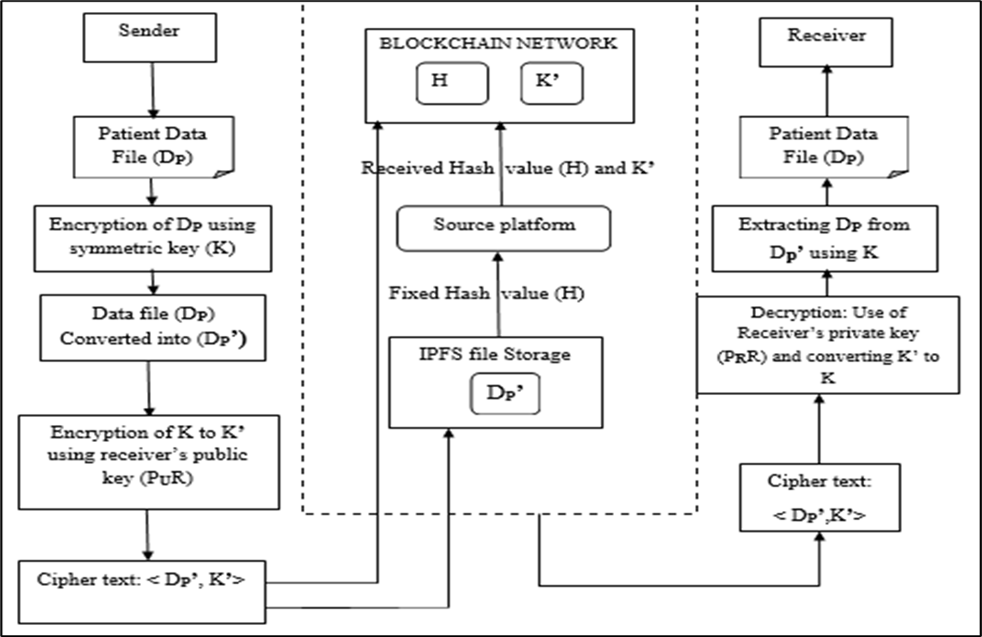
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the healthcare industry by enabling the seamless integration of medical devices, sensors, and data-driven applications. However, the large influx of sensitive healthcare data and the proliferation of linked devices have caused grave worries about data security and privacy. Traditional centralized security systems are unable to handle the changing threats and problems in the IoT healthcare setting. This study suggests a novel strategy for boosting data security in the healthcare industry that makes use of blockchain technology. The main goal of this research is to develop and deploy a trustworthy framework that safeguards private healthcare information in IoT networks. Blockchain, as a distributed and decentralized ledger, offers inherent security features such as immutability, transparency, and cryptographic mechanisms. In this research, it is suggested that healthcare data be gathered via the IoT and stored in the Interplanetary File System (IPFS) using Ethereum-based blockchain technology for data security. The suggested method creates a reliable environment for managing healthcare data by exploiting the special features of blockchain. The json and jpeg files are utilized five times on a distributed database housed on IPFS and a centralized database hosted on Firebase, and the upload and download times are recorded. For IoT-based healthcare systems, we have also investigated the cost and length of time required to implement smart contracts on blockchain platforms like Rinkeby, Binance, and Matic. This research suggests implementing the Blockchain platform in an IoT-based healthcare system to provide data confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility.
Article Details
References
. Singh, P. D., Dhiman, G., & Sharma, R. (2022). Internet of things for sustaining a smart and secure healthcare system. Sustainable computing: informatics and systems, 33, 100622.
. Salehi-Amiri, A., Jabbarzadeh, A., Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M., & Chaabane, A. (2022). Utilizing the Internet of Things (IoT) to address uncertain home health care supply chain network. Expert Systems with Applications, 208, 118239.
. Can, Y. S., & Ersoy, C. (2021). Privacy-preserving federated deep learning for wearable IoT-based biomedical monitoring. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology (TOIT), 21(1), 1-17.
. Singh, A. K., Anand, A., Lv, Z., Ko, H., & Mohan, A. (2021). A survey on healthcare data: a security perspective. ACM Transactions on Multimidia Computing Communications and Applications, 17(2s), 1-26.
. Esposito, C., De Santis, A., Tortora, G., Chang, H., & Choo, K. K. R. (2018). Blockchain: A panacea for healthcare cloud-based data security and privacy?. IEEE Cloud Computing, 5(1), 31-37.
. Sharma, P. K., Kumar, N., & Park, J. H. (2020). Blockchain technology toward green IoT: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Network, 34(4), 263-269.
. Biswas, K., & Muthukkumarasamy, V. (2016, December). Securing smart cities using blockchain technology. In 2016 IEEE 18th international conference on high performance computing and communications; IEEE 14th international conference on smart city; IEEE 2nd international conference on data science and systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS) (pp. 1392-1393). IEEE.
. Rathee, G., Sharma, A., Saini, H., Kumar, R., & Iqbal, R. (2020). A hybrid framework for multimedia data processing in IoT-healthcare using blockchain technology. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 79(15-16), 9711-9733.
. Ratta, P., Kaur, A., Sharma, S., Shabaz, M., & Dhiman, G. (2021). Application of blockchain and internet of things in healthcare and medical sector: applications, challenges, and future perspectives. Journal of Food Quality, 2021, 1-20.
. Dorri, A., Kanhere, S. S., Jurdak, R., & Gauravaram, P. (2017, March). Blockchain for IoT security and privacy: The case study of a smart home. In 2017 IEEE international conference on pervasive computing and communications workshops (PerCom workshops) (pp. 618-623). IEEE.
. Daraghmi, E. Y., Daraghmi, Y. A., & Yuan, S. M. (2019). MedChain: a design of blockchain-based system for medical records access and permissions management. IEEE Access, 7, 164595-164613.
. A. S. Rajawat, R. Rawat, K. Barhanpurkar, R. N. Shaw, and A. Ghosh, “Blockchain-Based Model for Expanding IoT Device Data Security,” Advances in Applications of Data-Driven Computing, pp. 61–71, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6919-1_5.
. S. Jiang, J. Cao, H. Wu, Y. Yang, M. Ma, and J. He, “Blochie: a Blockchain-based platform for healthcare information exchange,” in 2018 ieee international conference on smart computing (smartcomp). IEEE, 2018, pp. 49–56.
. El Majdoubi, D., El Bakkali, H., & Sadki, S. (2021). SmartMedChain: a blockchain-based privacy-preserving smart healthcare framework. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2021.
. J. Xu, K. Xue, S. Li, H. Tian, J. Hong, P. Hong, and N. Yu, “Healthchain: A Blockchain-based privacy preserving scheme for large-scale health data,” IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 8770–8781, 2019.
. Mohan, A., Prabha, G. ., & V., A. . (2023). Multi Sensor System and Automatic Shutters for Bridge- An Approach. International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering, 11(4s), 278–281. Retrieved from https://ijisae.org/index.php/IJISAE/article/view/2665
. K. M. Hossein, M. E. Esmaeili, T. Dargahi, A. Khonsari, and M. Conti, “Bchealth: A novel Blockchain-based privacy-preserving architecture for iot healthcare applications,” Computer Communications, vol. 180, pp. 31–47, 2021.
. K. Christodoulou, P. Christodoulou, Z. Zinonos, E. G. Carayannis, and S. A. Chatzichristofis, “Health information exchange with Blockchain amid covid-19-like pandemics,” in 2020 16th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (DCOSS). IEEE, 2020, pp. 412–417.
. Ghazal, T. M., Hasan, M. K., Abdullah, S. N. H. S., Bakar, K. A. A., & Al Hamadi, H. (2022). Private blockchain-based encryption framework using computational intelligence approach. Egyptian Informatics Journal, 23(4), 69-75.
. Khan, A. A., Bourouis, S., Kamruzzaman, M. M., Hadjouni, M., Shaikh, Z. A., Laghari, A. A., ... & Dhahbi, S. (2023). Data Security in Healthcare Industrial Internet of Things with Blockchain. IEEE Sensors Journal.
. Paul Garcia, Ian Martin, Laura López, Sigurðsson Ólafur, Matti Virtanen. Automated Grading Systems: Advancements and Challenges. Kuwait Journal of Machine Learning, 2(1). Retrieved from http://kuwaitjournals.com/index.php/kjml/article/view/165
. Chaudhury, S., & Sau, K. (2023). A blockchain-enabled internet of medical things system for breast cancer detection in healthcare. Healthcare Analytics, 100221.
. Patela, O., & Patelb, H. (2023). A Novel Approach to Address Data Security Concerns in the IoT Environment for Healthcare Domain using Blockchain Technology. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 38(3), 11.