Strategies and Approaches for Generating Identical Extensive XML Tree Instances
Main Article Content
Abstract
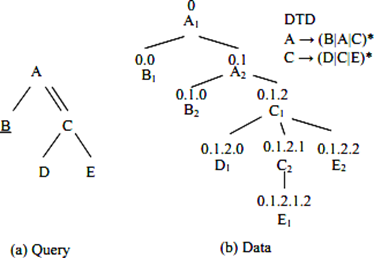
In recent years, XML has become the de facto internet wire language. Data may be organized and given context with the use of XML. A well-organized document facilitates the transformation of raw data into actionable intelligence. In B2B1 applications, the XML data is sent and created. This implies the need for fast query processing on XML data. The processing of XML tree sample queries (XTPQ) that provide an efficient response (also known as sample matching) is a topic of active study in the XML database field.DOM (Parser) may be used to transform an XML document into a tree representation. Extensible Markup Language (XML) query languages like XPath and XQuery use tree samples (twigs) to express query results.XML query processing focuses mostly on effectively locating all instances of twig 1 samples inside an XML database. Numerous techniques for matching such tree samples have been presented in recent years. In this study, we survey recent developments in XTPQ processing. This summary will begin by introducing several algorithms for twig sample matching and then go on to provide some background on holistic techniques to process XTPQ.
Article Details
References
. Berglund, S. Boag, and D. Chamberlin. XML path language (XPath) 2.0. W3C Recommendation 23 January 2007 http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath20/.
. S. Boag, D. Chamberlin, and M. F. Fernandez. Xquery 1.0: An XML query language. W3C Working Draft 22 August 2003.
. Choi, M. Mahoui, and D. Wood. On the optimality of the holistic twig join algorithms. In Proceeding of DEXA, pages 28–37, 2003.
. Zhang, J. F. Naughton, D. J. DeWitt, Q. Luo, and G. M. Lohman. On supporting containment queries in relational database management systems. In Proc. of SIGMODConference, pages 425-436, 2001.
. H. Wang, S. Park, W. Fan, and P. S. Yu. ViST: A dynamic index method for querying XML data by tree structures. In SIGMOD, pages 110-121, 2003.
. Singh, P. ., & Sharma, D. V. . (2023). Pre-Processing of Mobile Camera Captured Images for OCR . International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering, 11(2s), 147–155. Retrieved from https://ijisae.org/index.php/IJISAE/article/view/2518
. T. Yu, T. W. Ling, and J. Lu. Twigstacklistnot: A holistic twig join algorithm for twig query with not-predicates on xml data. In DASFAA, pages 249-263, 2006.
. H. V. Jagadish and S. AL-Khalifa. Timber: A native XML database. Technical report, University of Michigan, 2002.
. X. Wu, M. Lee, and W. Hsu. A prime number labeling scheme for dynamic ordered XML trees. In Proc. Of ICDE,pages 66-78, 2004.
. N. Bruno, D. Srivastava, and N. Koudas. Holistic twig joins: optimal XML sample matching. In Proc. of SIGMOD Conference, pages 310-321, 2002.
. Avinash, D. & Nalebuff, B. (1991). Thinking Strategically. New York: Norton & Co.
. Bicchieri A & Cristina J. (2007). Game Theory: Some Personal Reflections. In V.F. Hendricks and P.G.Hansen (eds.), Game Theory: 5 Questions, Copenhagen: Automatic Press.
. Binmore, K. (1991). Fun and Games: A Text on Game Theory. D.C.: Heath Lexington, MA.
. Binmore, K. (2007). Playing for Real: A Text on Game Theory. New York: OxfordUniversity Press.
. Brook, T. (2007). Computing the Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibria for Zero-Sum Games. Bath, U.K.: University of Bath.
. Davis, M. (1983). Game Theory: A Nontechnical Introduction. New York: Basic Books.
. Davis, M. (1997). Game Theory: A Non-Technical Introduction. New York: Dover Books.
. De Bruin, B. (2009). Over mathematisation in game theory: Pitting the Nash Equilibrium Refinement. Studies in History and Philosophy of Science, 40, 2-10.
. Dixit, A. K. and Nalebuff, B. J. (1991). Thinking Strategically: The Competitive Edge in Business, Politics, and Everyday Life. NewYork: Norton.
. Gilbbons, R. (1992). Game Theory for Applied Economics. New Jersey: Princeton University Press, Princeton.
. Gipin, A. & Sandholm, T. (2007). Lossless abstraction of imperfect information games. Journal of the ACM, 54(5), 2-29.
. Kelly, A. (2003). Decision Making using Game Theory: An Introduction for Managers. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
. Klempere, P. (1999). The Economic Theory of Auctions. London: Edward Elgar Lim, J.J. (1999). Fun, Games & Economics: An appraisal of game theory in economics. Undergraduate Journal of Economics, 3(1), 2-22.
. Fibonacci technique for privacy and security to sensitive data on cloud environment H Bommala, S Kiran, T Venkateswarlu, MAA Sheela - International Journal of Advanced Networking and …, 2020.