Zero-day Network Intrusion Detection using Machine Learning Approach
Main Article Content
Abstract
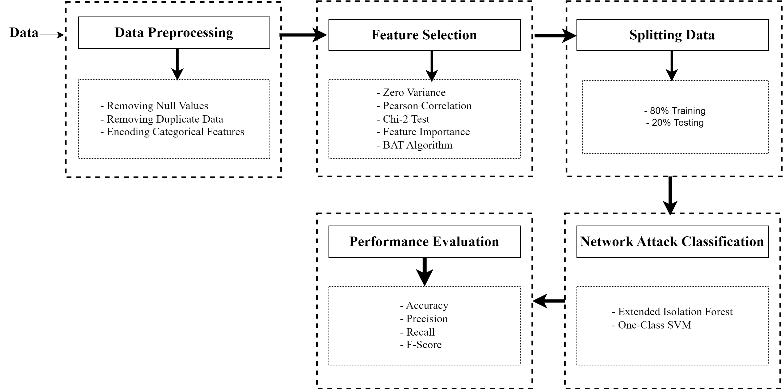
Zero-day network attacks are a growing global cybersecurity concern. Hackers exploit vulnerabilities in network systems, making network traffic analysis crucial in detecting and mitigating unauthorized attacks. However, inadequate and ineffective network traffic analysis can lead to prolonged network compromises. To address this, machine learning-based zero-day network intrusion detection systems (ZDNIDS) rely on monitoring and collecting relevant information from network traffic data. The selection of pertinent features is essential for optimal ZDNIDS performance given the voluminous nature of network traffic data, characterized by attributes. Unfortunately, current machine learning models utilized in this field exhibit inefficiency in detecting zero-day network attacks, resulting in a high false alarm rate and overall performance degradation. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces a novel approach combining the anomaly-based extended isolation forest algorithm with the BAT algorithm and Nevergrad. Furthermore, the proposed model was evaluated using 5G network traffic, showcasing its effectiveness in efficiently detecting both known and unknown attacks, thereby reducing false alarms when compared to existing systems. This advancement contributes to improved internet security.
Article Details
References
T. Shon and J. Moon, “A hybrid machine learning approach to network anomaly detection,” Inf. Sci., vol. 177, no. 18, pp. 3799-3821, Sept. 2007, doi:10.1016/j.ins.2007.03.025.
IBM, “Security X-force threat intelligence index 2023”. Available at: https://www.ibm.com/downloads/cas/DB4GL8YM.
A. L. Buczak and E. Guven, “A survey of data mining and machine learning methods for cyber security intrusion detection,” IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor., vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 1153-1176, 2016, doi:10.1109/COMST.2015.2494502.
A. Mukkamala et al., “Cyber security challenges: Designing efficient intrusion detection systems and antivirus tools” in Proc. of Enhancing Computer Security with Smart Technology, New York, NY, USA, 2005, pp. 125-163.
A. Sundaram, ‘An introduction to intrusion detection,’ Crossroads, vol. 2, no. 4, Apr. 1996, pp. 3-7.
A. Nisioti et al., “From intrusion detection to attacker attribution: A comprehensive survey of unsupervised methods,” IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor., vol. 20, no. 4, pp. 3369-3388, 2018, doi:10.1109/COMST.2018.2854724.
P. Casas et al., “Unsupervised network intrusion detection systems: Detecting the unknown without knowledge,” Comput. Commun., vol. 35, no. 7, pp. 772-783, 2012, doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2012.01.016.
I. Kang et al., “A differentiated oneclass classification method with applications to intrusion detection,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 3899-3905, 2012, doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2011.06.033.
F. Kuang et al., “A novel hybrid KPCA and SVM with GA model for intrusion detection,” Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 18, pp. 178-184, 2014, doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2014.01.028.
L. Wang and J. Shen, “A systematic review of bio-inspired service concretization,” IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 493-505, 2017, doi:10.1109/TSC.2015.2501300.
L. Wang et al., “Feed-back neural networks with discrete weights,” Neural Comput. Appl., vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 1063-1069, 2013, doi:10.1007/s00521-012-0867-8.
H. Hindy, et al., “Utilising deep LearningTechniques for effective zero-day attack detection,” Electronics, vol. 9, no. 10, p. 1684, 2020, doi:10.3390/electronics9101684.
L. Wang and J. Shen, “Data-intensive service provision based on particle swarm optimization,” Int. J. Comp. Intell. Syst., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 330-339, 2018, doi:10.2991/ijcis.11.1.25.
M. Sadiq and A. Khan, “Rule-based network intrusion detection using genetic algorithms,” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 26-29, 2011, doi:10.5120/2303-2914.
C. Wagner et al., “Machine learning approach for IP-flow record anomaly detection,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci., vol. 6640, pp. 28-39, 2011, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-20757-0_3.
I. Mbona and J. H. P. Eloff, “Detecting zero-day intrusion attacks using semi-supervised machine learning approaches,”, IEEE Access, vol. 10, 69822-69838, doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3187116.
N. Sameera and M. Shashi, “Deep transductive transfer learning framework for zero-day attack detection,” ICT Express, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 361-367, 2020, doi:10.1016/j.icte.2020.03.003.
H. Hindy et al., “‘Utilising deep learning techniques for effective zero-day attack detection,’ Electron.,”, Electronics, vol. 9, no. 10, pp. 1-16, 2020, doi:10.3390/electronics9101684.
N. Altwaijry et al., “A Deep Learning Approach for Anomaly-Based Network Intrusion Detection” Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci., vol. 1210 CCIS, pp. 603-615, 2020, doi:10.1007/978-981-15-7530-3_46.
D. P. Gaikwad and R. C. Thool, “‘Online Anomaly Based Intrusion Detection System Using Machine Learning,’ i-manager’s J. Cloud Comput,”, JCC, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 19-25, 2014, doi:10.26634/jcc.1.1.2800.
D. Oladimeji, “‘an Intrusion Detection System for Internet of,’ no,” Jun., pp. 1-25, 2021.
L. Bilge and T. Dumitra?, Before We Knew It: An Empirical Study of Zero-Day Attacks in the Real World, Proc. ACM Conf. Comput. Commun, 2012, pp. 833-844, doi:10.1145/2382196.2382284.
Thomas Wilson, Andrew Evans, Alejandro Perez, Luis Pérez, Juan Martinez. Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection and Outlier Analysis in Decision Science. Kuwait Journal of Machine Learning, 2(3). Retrieved from http://kuwaitjournals.com/index.php/kjml/article/view/207
M. Sarhan et al., “From zero-shot machine learning to zero-day attack detection,” Int. J. Inf. Secur., vol. 2023, no. Jun., 2019, doi:10.1007/s10207-023-00676-0.
H. Holm, “Signature based intrusion detection for zero-day attacks: (Not) A closed chapter?,” Proc. Annu. Hawaii Int. Conf., Syst. Sci., pp. 4895-4904, 2014, doi:10.1109/HICSS.2014.600.
J. Wang et al., “ClusterRep: A cluster-based reputation framework for balancing privacy and trust in vehicular participatory sensing,” Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw., vol. 14, no. 9, 2018, doi:10.1177/1550147718803299.
G. Nguyen et al., “Deep learning for proactive network monitoring and security protection,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 19696-19716, 2020, doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968718.
G. De La Torre Parra et al., “Detecting Internet of Things attacks using distributed deep learning,” J. Netw. Comput. Appl., vol. 163, no. Oct., 2020, doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102662.
X. Li et al., “Detection of low-frequency and multi-stage attacks in industrial Internet of things,” IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., vol. 69, no. 8, pp. 8820-8831, 2020, doi:10.1109/TVT.2020.2995133.
S. Moraboena et al., “A deep learning approach to network intrusion detection using deep autoencoder,” Rev. Intell. Artif., vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 457-463, 2020, doi:10.18280/ria.340410.
T. Wisanwanichthan and M. Thammawichai, “A double-layered hybrid approach for network intrusion detection system using combined naive Bayes and SVM,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 138432-138450, 2021, doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3118573.
I. Mbona and J. H. P. Eloff, “Detecting zero-day intrusion attacks using semi-supervised machine learning approaches,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, no. Apr., pp. 69822-69838, 2022, doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3187116.
M. A. Kabir and X. Luo, “Unsupervised learning for network flow based anomaly detection in the era of deep learning,” Proc 6th Int. Conf. Big Data Comput. Serv. Appl. Big Data Service 2020, vol. August 2020. IEEE, 2020, pp. 165-168, doi:10.1109/BigDataService49289.2020.00032.
S. Samarakoon et al., 2022, 5G-NIDD: A comprehensive network intrusion detection dataset generated over 5G wireless network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.01298.
K. Shaukat et al., “A survey on machine learning techniques for cyber security in the last decade,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 222310-222354, 2020, doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3041951, P. 222.
X.-S. Yang, “A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm” in Nature Inspired Cooperative Strategies for Optimization (NICSO 2010). Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2010, pp. 65-74, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-12538-6_6.
R. Abdulhammed et al., “Features dimensionality reduction approaches for machine learning based network intrusion detection,” Electronics, vol. 8, no. 3, p. 322, Mar. 2019, doi:10.3390/electronics8030322.
E. Druic? et al., “Benford’s law and the limits of digit analysis,” Int. J. Acc. Inf. Syst., vol. 31, pp. 75-82, Dec. 2018, doi:10.1016/j.accinf.2018.09.004.
M. F. Umer et al., “Flow-based intrusion detection: Techniques and challenges,” Comput. Secur., vol. 70, pp. 238-254, Sept. 2017, doi:10.1016/j.cose.2017.05.009.
G. Biau et al., “Nevergrad – A gradient-free optimization platform,” J. Mach. Learn. Res., vol. 21, no. 34, pp. 1-6, 2020.