Adapting Machine Learning Techniques for Developing Automatic Q&A Interaction Module for Translation Robots based on NLP
Main Article Content
Abstract
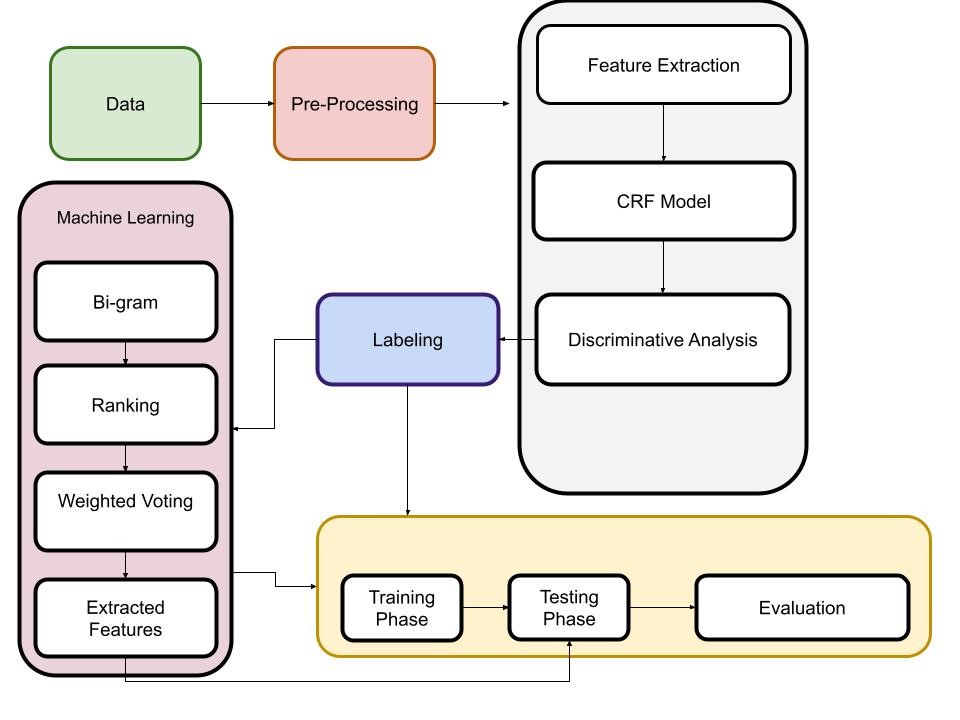
Research on Automatic Q&A Interaction Module of Computer-based Translation Robot is a study that focuses on developing an automatic question and answer (Q&A) interaction module for computer-based translation robots. The goal of the research is to enhance the capability of translation robots to perform more human-like interactions with users, particularly in terms of providing more efficient and accurate translations. In this paper proposed a Conditional Random Field Discriminative Analysis (CRFDA) for feature extraction to derive translation robot with Q&A. The proposed CRFDA model comprises of the discriminative analysis for the CRF model. The estimation CRF model uses the bi-directional classifier for the estimation of the feature vector. Finally, the classification is performed with the voting-based classification model for feature extraction. The performance of the CRFDA model is examined based on the Name Entity (Nes) in the TempVal1 &2 dataset. The extraction is based on the strict and relaxed feature model for the exact match and slight variation. The simulation analysis expressed that proposed CRFDA model achieves a classification accuracy of 91% which is significantly higher than the state-of-art techniques.
Article Details
References
Khurana, D., Koli, A., Khatter, K., & Singh, S. (2022). Natural language processing: State of the art, current trends and challenges. Multimedia tools and applications, 1-32.
Otter, D. W., Medina, J. R., & Kalita, J. K. (2020). A survey of the usages of deep learning for natural language processing. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, 32(2), 604-624.
Raina, V., & Krishnamurthy, S. (2022). Natural language processing. In Building an Effective Data Science Practice (pp. 63-73). Apress, Berkeley, CA.
Wolf, T., Debut, L., Sanh, V., Chaumond, J., Delangue, C., Moi, A., ... & Rush, A. M. (2020, October). Transformers: State-of-the-art natural language processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing: system demonstrations (pp. 38-45).
Galassi, A., Lippi, M., & Torroni, P. (2020). Attention in natural language processing. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 32(10), 4291-4308.
Qiu, X., Sun, T., Xu, Y., Shao, Y., Dai, N., & Huang, X. (2020). Pre-trained models for natural language processing: A survey. Science China Technological Sciences, 63(10), 1872-1897.
Qi, P., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Bolton, J., & Manning, C. D. (2020). Stanza: A Python natural language processing toolkit for many human languages. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07082.
Cui, Y., Che, W., Liu, T., Qin, B., Wang, S., & Hu, G. (2020). Revisiting pre-trained models for Chinese natural language processing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.13922.
Torfi, A., Shirvani, R. A., Keneshloo, Y., Tavaf, N., & Fox, E. A. (2020). Natural language processing advancements by deep learning: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.01200.
Gu, Y., Tinn, R., Cheng, H., Lucas, M., Usuyama, N., Liu, X., ... & Poon, H. (2021). Domain-specific language model pretraining for biomedical natural language processing. ACM Transactions on Computing for Healthcare (HEALTH), 3(1), 1-23.
Guo, J., He, H., He, T., Lausen, L., Li, M., Lin, H., ... & Zhu, Y. (2020). GluonCV and GluonNLP: Deep Learning in Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 21(23), 1-7.
Wu, S., Roberts, K., Datta, S., Du, J., Ji, Z., Si, Y., ... & Xu, H. (2020). Deep learning in clinical natural language processing: a methodical review. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 27(3), 457-470.
Yang, L., Li, Y., Wang, J., &Sherratt, R. S. (2020). Sentiment analysis for E-commerce product reviews in Chinese based on sentiment lexicon and deep learning. IEEE Access, 8, 23522-23530.
Yadav, A., & Vishwakarma, D. K. (2020). Sentiment analysis using deep learning architectures: a review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 53(6), 4335-4385.
Xu, G., Meng, Y., Qiu, X., Yu, Z., & Wu, X. (2019). Sentiment analysis of comment texts based on BiLSTM. Ieee Access, 7, 51522-51532.
Do, H. H., Prasad, P. W. C., Maag, A., &Alsadoon, A. (2019). Deep learning for aspect-based sentiment analysis: a comparative review. Expert Systems with Applications, 118, 272-299.
Dang, N. C., Moreno-García, M. N., & De la Prieta, F. (2020). Sentiment analysis based on deep learning: A comparative study. Electronics, 9(3), 483.
Phan, H. T., Tran, V. C., Nguyen, N. T., & Hwang, D. (2020). Improving the performance of sentiment analysis of tweets containing fuzzy sentiment using the feature ensemble model. IEEE Access, 8, 14630-14641.
Danilevsky, M., Qian, K., Aharonov, R., Katsis, Y., Kawas, B., & Sen, P. (2020). A survey of the state of explainable AI for natural language processing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.00711.
Rajput, A. (2020). Natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and clinical analytics. In Innovation in Health Informatics (pp. 79-97). Academic Press.
Giménez, M., Palanca, J., & Botti, V. (2020). Semantic-based padding in convolutional neural networks for improving the performance in natural language processing. A case of study in sentiment analysis. Neurocomputing, 378, 315-323.
Oueslati, O., Cambria, E., HajHmida, M. B., & Ounelli, H. (2020). A review of sentiment analysis research in Arabic language. Future Generation Computer Systems, 112, 408-430.
Guo, J., He, H., He, T., Lausen, L., Li, M., Lin, H., ... & Zhu, Y. (2020). GluonCV and GluonNLP: Deep Learning in Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 21(23), 1-7.
Guo, J., He, H., He, T., Lausen, L., Li, M., Lin, H., ... & Zhu, Y. (2020). GluonCV and GluonNLP: Deep Learning in Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 21(23), 1-7.
Nemes, L., & Kiss, A. (2021). Social media sentiment analysis based on COVID-19. Journal of Information and Telecommunication, 5(1), 1-15.
Torfi, A., Shirvani, R. A., Keneshloo, Y., Tavaf, N., & Fox, E. A. (2020). Natural language processing advancements by deep learning: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.01200.
Otter, D. W., Medina, J. R., & Kalita, J. K. (2020). A survey of the usages of deep learning for natural language processing. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, 32(2), 604-624.
Manguri, K. H., Ramadhan, R. N., & Amin, P. R. M. (2020). Twitter sentiment analysis on worldwide COVID-19 outbreaks. Kurdistan Journal of Applied Research, 54-65.