Exploiting Emotions via Composite Pretrained Embedding and Ensemble Language Model
Main Article Content
Abstract
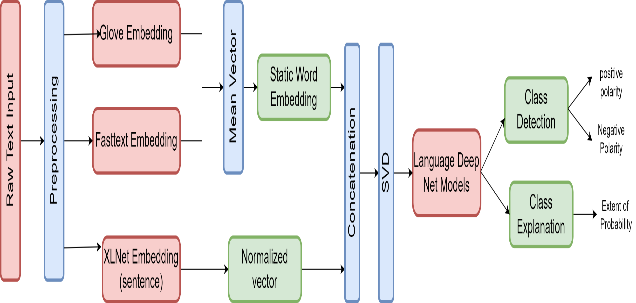
Decisions in the modern era are based on more than just the available data; they also incorporate feedback from online sources. Processing reviews known as Sentiment analysis (SA) or Emotion analysis. Understanding the user's perspective and routines is crucial now-a-days for multiple reasons. It is used by both businesses and governments to make strategic decisions. Various architectural and vector embedding strategies have been developed for SA processing. Accurate representation of text is crucial for automatic SA. Due to the large number of languages spoken and written, polysemy and syntactic or semantic issues were common. To get around these problems, we developed effective composite embedding (ECE), a method that combines the advantages of vector embedding techniques that are either context-independent (like glove & fasttext) or context-aware (like XLNet) to effectively represent the features needed for processing. To improve the performace towards emotion or sentiment we proposed stacked ensemble model of deep lanugae models.ECE with Ensembled model is evaluated on balanced dataset to prove that it is a reliable embedding technique and a generalised model for SA.In order to evaluate ECE, cutting-edge ML and Deep net language models are deployed and comapared. The model is evaluated using benchmark datset such as MR, Kindle along with realtime tweet dataset of user complaints . LIME is used to verify the model's predictions and to provide statistical results for sentence.The model with ECE embedding provides state-of-art results with real time dataset as well.
Article Details
References
Xu, Y., Ren, J., Wang, G., Zhang, C., Yang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2019). A blockchain-based nonrepudiation network computing service scheme for industrial IoT. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15(6), 3632-3641.
O'Connor, B., Balasubramanyan, R., Routledge, B. R., & Smith, N. A. (2010, May). From tweets to polls: Linking text sentiment to public opinion time series. In Fourth international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media.
Liu, B. (2015). Sentiment analysis: Mining opinions, sentiments, and emotions. Cambridge: CUP. Go to original source..
Pang, B., & Lee, L. (2004). A sentimental education: Sentiment analysis using subjectivity summarization based on minimum cuts. arXiv preprint cs/0409058. Elissa, “Title of paper if known,” unpublished.
Teng, Z., Vo, D. T., & Zhang, Y. (2016, November). Context-sensitive lexicon features for neural sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (pp. 1629-1638).
Yan, K., Zhong, C., Ji, Z., & Huang, J. (2018). Semi-supervised learning for early detection and diagnosis of various air handling unit faults. Energy and Buildings, 181, 75-83.
Lu, H., Yang, L., Yan, K., Xue, Y., & Gao, Z. (2017). A cost-sensitive rotation forest algorithm for gene expression data classification. Neurocomputing, 228, 270-276.
Huang, Q., Chen, R., Zheng, X., & Dong, Z. (2017, August). Deep sentiment representation based on CNN and LSTM. In 2017 international conference on green informatics (ICGI) (pp. 30-33). IEEE.
Neethu, M. S., & Rajasree, R. (2013, July). Sentiment analysis in twitter using machine learning techniques. In 2013 fourth international conference on computing, communications and networking technologies (ICCCNT) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Xia, H., Yang, Y., Pan, X., Zhang, Z., & An, W. (2020). Sentiment analysis for online reviews using conditional random fields and support vector machines. Electronic Commerce Research, 20(2), 343-360.
Qu, L., Ifrim, G., & Weikum, G. (2010, August). The bag-of-opinions method for review rating prediction from sparse text patterns. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics (Coling 2010) (pp. 913-921).
Campos, V., Jou, B., & Giro-i-Nieto, X. (2017). From pixels to sentiment: Fine-tuning CNNs for visual sentiment prediction. Image and Vision Computing, 65, 15-22.
Schmidhuber, J. (2015). Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural networks, 61, 85-117.
Marasek, K. (2015). Deep belief neural networks and bidirectional long-short term memory hybrid for speech recognition. Archives of Acoustics, 40(2), 191-195.
Jawale, S., & Sawarkar, S. D. (2020, December). Interpretable Sentiment Analysis based on Deep Learning: An overview. In 2020 IEEE Pune Section International Conference (PuneCon) (pp. 65-70). IEEE.
Goldberg, Y. (2016). A primer on neural network models for natural language processing. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 57, 345-420.
Jawale, S., & Sawarkar, S. D. (2023). Sentiment Analysis and Vector Embedding: A Comparative Study. In Smart Trends in Computing and Communications (pp. 311-321). Springer, Singapore.
Hameed, Z., & Garcia-Zapirain, B. (2020). Sentiment classification using a single-layered BiLSTM model. Ieee Access, 8, 73992-74001.
Gupta, P., & Jaggi, M. (2021). Obtaining better static word embeddings using contextual embedding models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.04302.
Zhang, L., Wang, S., & Liu, B. (2018). Deep learning for sentiment analysis: A survey. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 8(4), e1253.
Al-Moslmi, T., Omar, N., Abdullah, S., & Albared, M. (2017). Approaches to cross-domain sentiment analysis: A systematic literature review. Ieee access, 5, 16173-16192.
T. Mikolov, K. Chen, G. Corrado, J. Dean, “Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space,” Proc. Workshop at ICLR, 2013.
T. Mikolov, W.Yih, G. Zweig, “Linguistic Regularities in Continuous Space Word Representations,” Proc. NAACL HLT, 2013.
T. Mikolov, I. Sutskever, K. Chen, G. Corrado, J. Dean, “Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality,” Proc.
Pennington, J., Socher, R., & Manning, C. D. (2014, October). Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP) (pp. 1532-1543).
Piotr Bojanowski, Edouard Grave, Armand Joulin, and Tomas Mikolov. 2017.Enriching word vectors with subword information. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics 5 (2017), 135–146
Matthew Peters, Mark Neumann, Mohit Iyyer, Matt Gardner, Christopher Clark, Kenton Lee, and Luke Zettlemoyer. 2018a. Deep contextualized word representations. In NAACL
Han, Xu, et al. "Pre-trained models: Past, present and future." AI Open 2 (2021): 225-250.
Devlin, J., Chang, M. W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805.
Lan, Z., Chen, M., Goodman, S., Gimpel, K., Sharma, P., & Soricut, R. (2019). Albert: A lite bert for self-supervised learning of language representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.11942.
Yang, Z., Dai, Z., Yang, Y., Carbonell, J., Salakhutdinov, R. R., & Le, Q. V. (2019). Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. Advances in neural information processing systems, 32.
Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. Advances in neural information processing systems, 32.
Jawale, S. S., & Sawarker, S. D. (2022). Amalgamation of Embeddings With Model Explainability for Sentiment Analysis. International Journal of Applied Evolutionary Computation (IJAEC), 13(1), 1-24.
Ghannay, S., Favre, B., Esteve, Y., & Camelin, N. (2016, May). Word embedding evaluation and combination. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC'16) (pp. 300-305).
Khasanah, I. N. (2021). Sentiment Classification Using fastText Embedding and Deep Learning Model. Procedia Computer Science, 189, 343-350.
Deep Learning Model. Procedia Computer Science, 189, 343-350.
Tulio Ribeiro, M., Singh, S., & Guestrin, C. (2016). " Why Should I Trust You?": Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. ArXiv e-prints, arXiv-1602.
Li, J., Chen, X., Hovy, E., & Jurafsky, D. (2015). Visualizing and understanding neural models in nlp. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.01066.
Liu, H., & Cocea, M. (2017). Fuzzy information granulation towards interpretable sentiment analysis. Granular Computing, 2(4), 289-302.
Pota, M., Ventura, M., Catelli, R., & Esposito, M. (2020). An effective BERT-based pipeline for Twitter sentiment analysis: A case study in Italian. Sensors, 21(1), 133.
Dorle, S., & Pise, N. N. (2017). Sentiment Analysis Methods and Approach: Survey. International Journal of Innovative Computer Science & Engineering, 4(6), 7-11.
Ganaie, M. A., Hu, M., Malik, A. K., Tanveer, M., & Suganthan, P. N. (2022). Ensemble deep learning: A review. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 115, 105151.
S. B, S. S, G. D. T and V. R. N, "Sentiment Analysis on Movie Reviews: A Comparative Analysis," 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Communication, IoT and Security (ICISCoIS), Coimbatore, India, 2023, pp. 218-223. doi: 10.1109/ICISCoIS56541.2023.10100367
Kamruzzaman, M., Hossain, M., Imran, M. R. I., & Bakchy, S. C. (2021, August). A comparative analysis of sentiment classification based on deep and traditional ensemble machine learning models. In 2021 International Conference on Science & Contemporary Technologies (ICSCT) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
.Hassan, A., & Mahmood, A. (2018). Convolutional recurrent deep learning model for sentence classification. Ieee Access, 6, 13949-13957.
Joachims, T. (1998, April). Text categorization with support vector machines: Learning with many relevant features. In European conference on machine learning (pp. 137-142). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Prabha, M. I., & Srikanth, G. U. (2019, April). Survey of sentiment analysis using deep learning techniques. In 2019 1st International Conference on Innovations in Information and Communication Technology (ICIICT) (pp. 1-9). IEEE.
Z. Z. Wint, Y. Manabe and M. Aritsugi,2018 IEEEInternational Conference on Big Data, Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (BCD), Yonago, 2018, pp. 91-96.
Huy Nguyen and Minh-Le Nguyen,K. Hasida and W. P. Pa (Eds.): PACLING 2017, Communications in computer and information science (CCIS), vol 781, pp. 15–27, 2018.
Jianqiang, Z., Xiaolin, G., & Xuejun, Z. (2018). Deep convolution neural networks for twitter sentiment analysis. IEEE access, 6, 23253-23260.
Wei Xue, Tao Li in Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Long Papers), pages 2514– 2523 Melbourne, Australia, July 15 - 20, 2018
Jianqiang, Z., Xiaolin, G., & Xuejun, Z. (2018). Deep convolution neural networks for twitter sentiment analysis. IEEE access, 6, 23253-23260.
A. Onaciu and A. Nicoleta Marginean 2018 IEEE 14th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing (ICCP), Cluj-Napoca, 2018, pp. 13-19
Ganaie, M. A., Hu, M., Malik, A. K., Tanveer, M., & Suganthan, P. N. (2022). Ensemble deep learning: A review. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 115, 105151.
N. Aslam, F. Rustam, E. Lee, P. B. Washington and I. Ashraf, "Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Detection on Cryptocurrency Related Tweets Using Ensemble LSTM-GRU Model," in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 39313-39324, 2022. doi: 10.1109/ ACCESS.2022. 3165621.
Baroni, M., Dinu, G., & Kruszewski, G. (2014, June). Don’t count, predict! a systematic comparison of context-counting vs. context-predicting semantic vectors. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) (pp. 238-247).
Roman, M., Shahid, A., Khan, S., Koubaa, A., & Yu, L. (2021). Citation intent classification using word embedding. Ieee Access, 9, 9982-9995.
Jawale and Sawarkar,"Word Embedding and Intent Analysis: A Literature Survey (2022)",http://www.gisscience.net/VOLUME-9-ISSUE-2-2022/, DOI:20.18001.GSJ.2022.V9I2.22.38707
Bollegala, D., & O'Neill, J. (2022). A Survey on Word Meta-Embedding Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.11660.
Tan, K. L., Lee, C. P., Lim, K. M., & Anbananthen, K. S. M. (2022). Sentiment analysis with ensemble hybrid deep learning model. IEEE Access, 10, 103694-103704..
Yesir, S., & So?ukpinar, ?. (2021, June). Malware Detection and Classification Using fastText and BERT. In 2021 9th International Symposium on Digital Forensics and Security (ISDFS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Sheng, D., & Yuan, J. (2021, May). An efficient long Chinese text sentiment analysis method using BERT-based models with BiGRU. In 2021 IEEE 24th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD) (pp. 192-197). IEEE.
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Yu, L. C., & Zhang, X. (2022). Contextual sentiment embeddings via bi-directional GRU language model. Knowledge-Based Systems, 235, 107663.
Dedhia, C., & Ramteke, J. (2017, January). Ensemble model for Twitter sentiment analysis. In 2017 International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Ghannay, S., Favre, B., Esteve, Y., & Camelin, N. (2016, May). Word embedding evaluation and combination. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC'16) (pp. 300-305).
Alharbi, A. I., Smith, P., & Lee, M. (2021). Enhancing contextualised language models with static character and word embeddings for emotional intensity and sentiment strength detection in arabic tweets. Procedia Computer Science, 189, 258-265.
Waheeb , M. Q. ., SANGEETHA, D., & Raj , R. . (2021). Detection of Various Plant Disease Stages and Its Prevention Method Based on Deep Learning Technique. Research Journal of Computer Systems and Engineering, 2(2), 33:37. Retrieved from https://technicaljournals.org/RJCSE/index.php/journal/article/view/30
Da Silva, N.F.F., Hruschka, E.R., Hruschka, E.R.: Tweet sentiment analysis with classifier ensembles. Decis. Support Syst. 66, 170–179 (2014) (2014): 1093-1113
Basiri, M. E., Nemati, S., Abdar, M., Cambria, E., & Acharya, U. R. (2021). ABCDM: An attention-based bidirectional CNN-RNN deep model for sentiment analysis. Future Generation Computer Systems, 115, 279-294
Wall, M. E., Rechtsteiner, A., & Rocha, L. M. (2003). Singular value decomposition and principal component analysis. In A practical approach to microarray data analysis (pp. 91-109). Springer, Boston, MA
Sukhbaatar, S., Weston, J., & Fergus, R. (2015). End-to-end memory networks. Advances in neural information processing systems, 28.
Guo, B., Zhang, C., Liu, J., & Ma, X. (2019). Improving text classification with weighted word embeddings via a multi-channel TextCNN model. Neurocomputing, 363, 366-374.
He, R., & McAuley, J. (2016, April). Ups and downs: Modeling the visual evolution of fashion trends with one-class collaborative filtering. In proceedings of the 25th international conference on world wide web (pp. 507-517).
N. Srivastava, G. Hinton, A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, andR. Salakhutdinov, ‘‘Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networksfrom over?tting,’’ J. Mach. Learn. Res., vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 1958–7929,2014
Prechelt, L. (2002). Early stopping-but when?. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the trade (pp. 55-69). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Dessì, D., Dragoni, M., Fenu, G., Marras, M., & Recupero, D. R. (2019, April). Evaluating neural word embeddings created from online course reviews for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 34th ACM/SIGAPP symposium on applied computing (pp. 2124-2127).
Yoon, K. (2014). Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification [OL]. arXiv Preprint.
Hochreiter, S., & Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term memory. Neural computation, 9(8), 1735-1780.
Rao, G., Huang, W., Feng, Z., & Cong, Q. (2018). LSTM with sentence representations for document-level sentiment classification. Neurocomputing, 308, 49-57.
Xu, G., Meng, Y., Qiu, X., Yu, Z., & Wu, X. (2019). Sentiment analysis of comment texts based on BiLSTM. Ieee Access, 7, 51522-51532.
Long, Y., Li, Y., Luo, J., Miao, C., & Fu, J. (2019, November). MCP-LSTM Network for Sentence-Level Sentiment Classification. In 2019 International Conference on Virtual Reality and Visualization (ICVRV) (pp. 124-128). IEEE.
Zouzou, A., & El Azami, I. (2021, October). Text sentiment analysis with CNN & GRU model using GloVe. In 2021 Fifth International Conference On Intelligent Computing in Data Sciences (ICDS) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Salur, M. U., & Aydin, I. (2020). A novel hybrid deep learning model for sentiment classification. IEEE Access, 8, 58080-58093.
Alghanmi, I., Espinosa-Anke, L., & Schockaert, S. (2020). Combining BERT with static word embeddings for categorizing social media.