Mental State Prediction Using Machine Learning and EEG Signal
Main Article Content
Abstract
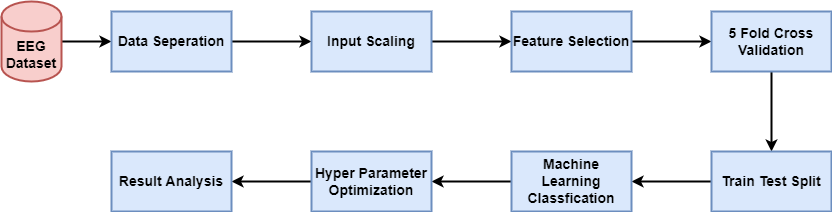
One of the most exciting areas of computer science right now is brain-computer interface (BCI) research. A conduit for data flow between both the brain as well as an electronic device is the brain-computer interface (BCI). Researchers in several disciplines have benefited from the advancements made possible by brain-computer interfaces. Primary fields of study include healthcare and neuroergonomics. Brain signals could be used in a variety of ways to improve healthcare at every stage, from diagnosis to rehabilitation to eventual restoration. In this research, we demonstrate how to classify EEG signals of brain waves using machine learning algorithms for predicting mental health states. The XGBoost algorithm's results have an accuracy of 99.62%, which is higher than that of any other study of its kind and the best result to date for diagnosing people's mental states from their EEG signals. This discovery will aid in taking efforts [1] to predict mental state using EEG signals to the next level.
Article Details
References
J. B. F. Van Erp, F. Lotte, and M. Tangermann, “Brain-computer interfaces: Beyond medical applications,” Computer (Long. Beach. Calif)., vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 26–34, Apr. 2012, doi: 10.1109/MC.2012.107.
R. Rao and R. Scherer, “Brain-Computer Interfacing,” IEEE Signal Process. Mag., vol. 27, no. 4, 2010, doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936774.
L. Bi, X. A. Fan, and Y. Liu, “EEG-based brain-controlled mobile robots: A survey,” IEEE Trans. Human-Machine Syst., vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 161–176, Mar. 2013, doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2012.2219046.
N. Sheehy, “Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications and Related Fields,” J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, vol. 47, no. 6, pp. 654–654, 1984, doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.6.654-a.
L. A. Jorgenson et al., “The BRAIN Initiative: developing technology to catalyse neuroscience discovery,” Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci., vol. 370, no. 1668, May 2015, doi: 10.1098/RSTB.2014.0164.
J. Ashford, J. Bird, F. Campelo, and D. Faria, “Classification of EEG Signals Based on Image Representation of Statistical Features,” 2020, pp. 449–460.
M. Faezipour, M. Faezipour, N. Vanello, and A. Lanata, “Efficacy of Smart EEG Monitoring Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic,” Electron. 2021, Vol. 10, Page 1001, vol. 10, no. 9, p. 1001, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.3390/ELECTRONICS10091001.
A. Badarin, V. Skazkina, and V. Grubov, Studying of human’s mental state during visual information processing with combined EEG and fNIRS. 2020.
M. R. Farazi, F. Faisal, Z. Zaman, and S. Farhan, “Inpainting multiple sclerosis lesions for improving registration performance with brain atlas,” 1st Int. Conf. Med. Eng. Heal. Informatics Technol. MediTec 2016, Jan. 2017, doi: 10.1109/MEDITEC.2016.7835363.
F. Faisal and M. Nishat, “An Investigation for Enhancing Registration Performance with Brain Atlas by Novel Image Inpainting Technique using Dice and Jaccard Score on Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Tissue,” Biomed. Pharmacol. J., vol. 12, pp. 1249–1262, Sep. 2019, doi: 10.13005/bpj/1754.
M. A. Asif et al., “Performance Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Cardiovascular Disease,” Eng. Lett., vol. 29, pp. 731–741, May 2021.
F. Faisal, M. M. Nishat, M. A. Mahbub, M. M. I. Shawon, and M. M. U. H. Alvi, “Covid-19 and its impact on school closures: A predictive analysis using machine learning algorithms,” 2021 Int. Conf. Sci. Contemp. Technol. ICSCT 2021, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ICSCT53883.2021.9642617.
M. M. Nishat and F. Faisal, “An investigation of spectroscopic characterization on biological tissue,” 4th Int. Conf. Electr. Eng. Inf. Commun. Technol. iCEEiCT 2018, pp. 290–295, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.1109/CEEICT.2018.8628081.
M. A. A. R. Asif et al., “Computer aided diagnosis of thyroid disease using machine learning algorithms,” Proc. 2020 11th Int. Conf. Electr. Comput. Eng. ICECE 2020, pp. 222–225, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1109/ICECE51571.2020.9393054.
M. M. Nishat et al., “Performance Investigation of Different Boosting Algorithms in Predicting Chronic Kidney Disease,” 2020 2nd Int. Conf. Sustain. Technol. Ind. 4.0, STI 2020, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1109/STI50764.2020.9350440.
A. Kishor and C. Chakraborty, “Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Based Healthcare 4.0 Monitoring System,” Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, pp. 1–17, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.1007/S11277-021-08708-5.
P. Bashivan, I. Rish, and S. Heisig, “Mental State Recognition via Wearable EEG,” Feb. 2016, doi: 10.48550/arxiv.1602.00985.
D. Steyrl, G. Krausz, and K. Koschutnig, “Early Stress Detection and Analysis using EEG signals in Machine Learning Framework,” IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 1116, no. 1, p. 012134, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/1116/1/012134.
J. J. Bird, D. R. Faria, L. J. Manso, A. Ekárt, and C. D. Buckingham, “A deep evolutionary approach to bioinspired classifier optimisation for brain-machine interaction,” Complexity, vol. 2019, 2019, doi: 10.1155/2019/4316548.
R. Richer, N. Zhao, J. Amores, B. M. Eskofier, and J. A. Paradiso, “Real-time Mental State Recognition using a Wearable EEG,” Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. Annu. Int. Conf., vol. 2018, pp. 5495–5498, Jul. 2018, doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8513653.
X. Wu et al., “EEG based mental state analysis,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 1911, no. 1, p. 012014, May 2021, doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1911/1/012014.
S. Ghosh-Dastidar and H. Adeli, “Improved spiking neural networks for EEG classification and epilepsy and seizure detection,” Integr. Comput. Aided. Eng., vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 187–212, 2007, doi: 10.3233/ICA-2007-14301.
D. Dadebayev, W. W. Goh, and E. X. Tan, “EEG-based emotion recognition: Review of commercial EEG devices and machine learning techniques,” J. King Saud Univ. - Comput. Inf. Sci., vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 4385–4401, Jul. 2021, doi: 10.1016/J.JKSUCI.2021.03.009.
S. Koelstra et al., “Single trial classification of EEG and peripheral physiological signals for recognition of emotions induced by music videos,” Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 6334 LNAI, pp. 89–100, 2010, doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-15314-3_9/COVER.
D. R. Edla, K. Mangalorekar, G. Dhavalikar, and S. Dodia, “Classification of EEG data for human mental state analysis using Random Forest Classifier,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 132, pp. 1523–1532, Jan. 2018, doi: 10.1016/J.PROCS.2018.05.116.
C. Y. Jin, J. P. Borst, and M. K. van Vugt, “Distinguishing vigilance decrement and low task demands from mind?wandering: A machine learning analysis of EEG,” Eur. J. Neurosci., vol. 52, no. 9, p. 4147, Nov. 2020, doi: 10.1111/EJN.14863.
H. Zeng, C. Yang, G. Dai, F. Qin, J. Zhang, and W. Kong, “EEG classification of driver mental states by deep learning,” Cogn. Neurodynamics 2018 126, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 597–606, Jul. 2018, doi: 10.1007/S11571-018-9496-Y.
D. H. Lee, J. H. Jeong, K. Kim, B. W. Yu, and S. W. Lee, “Continuous EEG Decoding of Pilots’ Mental States Using Multiple Feature Block-Based Convolutional Neural Network,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 121929–121941, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3006907.
M. Gulhane and T. Sajana, “Human Behavior Prediction and Analysis Using Machine Learning-A Review,” Turkish J. Comput. Math. Educ., vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 870–876, Apr. 2021, doi: 10.17762/TURCOMAT.V12I5.1499.
J. J. Bird, L. J. Manso, E. P. Ribeiro, A. Ekart, and D. R. Faria, “A Study on Mental State Classification using EEG-based Brain-Machine Interface,” 9th Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. 2018 Theory, Res. Innov. Appl. IS 2018 - Proc., pp. 795–800, Jul. 2018, doi: 10.1109/IS.2018.8710576.
P. Rani, R. Kumar, A. Jain, and R. Lamba, “Taxonomy of Machine Learning Algorithms and Its Applications,” J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci., vol. 17, no. 6, pp. 2508–2513, Sep. 2020, doi: 10.1166/JCTN.2020.8922.
M. A. Jabbar, B. L. Deekshatulu, and P. Chandra, “Prediction of heart disease using random forest and feature subset selection,” Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput., vol. 424, pp. 187–196, 2016, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-28031-8_16.
“XGBoost Algorithm | XGBoost In Machine Learning.” https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2018/09/an-end-to-end-guide-to-understand-the-math-behind-xgboost/ (accessed Jan. 13, 2022).
I. D. Mienye, Y. Sun, and Z. Wang, “Improved sparse autoencoder based artificial neural network approach for prediction of heart disease,” Informatics Med. Unlocked, vol. 18, p. 100307, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/J.IMU.2020.100307.
J. Bird, A. Ekart, C. Buckingham, and D. Faria, Mental Emotional Sentiment Classification with an EEG-based Brain-machine Interface. 2019.
A. A. Rahman et al., “Detection of Mental State from EEG Signal Data: An Investigation with Machine Learning Classifiers,” KST 2020 - 2021 14th Int. Conf. Knowl. Smart Technol., pp. 152–166, 2022, doi: 10.1109/KST53302.2022.9729084.
V. Vijean, M. Hariharan, A. Saidatul, and S. Yaacob, “Mental tasks classifications using S-transform for BCI applications,” 2011 IEEE Conf. Sustain. Util. Dev. Eng. Technol. STUDENT 2011, pp. 69–73, 2011, doi: 10.1109/STUDENT.2011.6089327.