Conversational AI for Natural Language Processing: An Review of ChatGPT
Main Article Content
Abstract
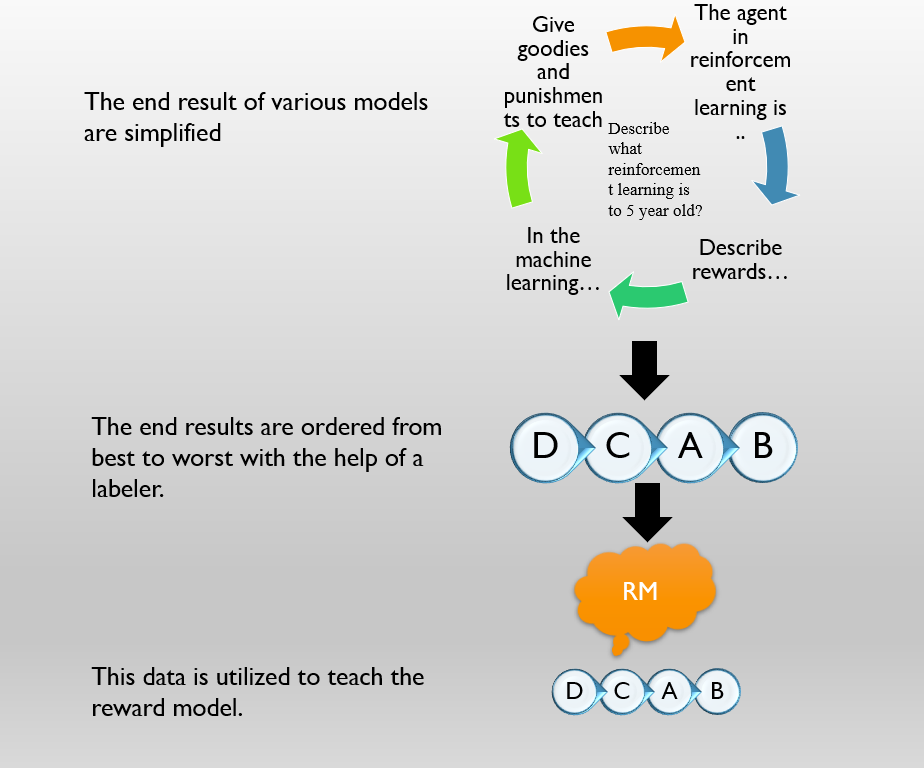
ChatGPT is a conversational artificial intelligence model developed by OpenAI, which was introduced in 2019. It employs a transformer-based neural mesh to produce human being responses in real-time, allowing for natural language conversations with a machine. ChatGPT is instructed on huge quantities of data captured using the internet, making it knowledgeable in an extensive span of topics, from news & entertainment to politics and sports. This allows it to generate contextually relevant responses to questions and statements, making the conversation seem more lifelike. The model can be used in various applications, including customer service, personal assistants, and virtual assistants. ChatGPT has also shown promising results in generating creative content, such as jokes and poetry, showcasing its versatility and potential for future applications.
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the existing literature on ChatGPT, highlighting its key advantages, such as improved accuracy and flexibility compared to traditional NLP tools, as well as its limitations and the need for further research to address potential ethical concerns. The review also highlights the potential for ChatGPT to be used in NLP applications, including question-answering and dialogue generation, and highlights the need for further research and development in these areas.
Article Details
References
Brown, T. B., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P., ... & Amodei, D. (2020). Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.14165.
Rajpurkar, P., Jia, R., Liang, P., & Schiebinger, L. (2018). Know what you don’t know: Unanswerable questions for SQuAD. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.03822.
Devlin, J., Chang, M. W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2018). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., ... & Bengio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 2672-2680).
Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., & Sutskever, I. (2019). Language models are unsupervised multitask learners.