Prediction of Factors Influencing Social Performance of Indian MFIs using Machine Learning Approach
Main Article Content
Abstract
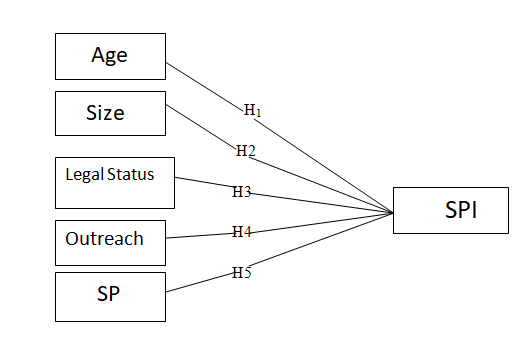
The aim of the current work is to predict the impact of MFI specific internal factors on the social performance of Indian microfinance institutions (MFIs) by using machine learning techniques. Social performance index (SPI) is designed by taking data of 73 Indian MFIs for 10 years with the help of an indexing technique where six different factors (operational self sufficiency, number of women borrowers, number of rural borrowers, gross loan portfolio, average loan balance per borrower / GNI per capita and cost per borrower) representing different dimensions of functioning of MFIs are considered. The data is taken from MIX data repository. Pooled OLS regression model is used for analyzing impact of various MFI specific factors on SPI. For predicting the SPI, Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) machine learning model is considered that takes all independent variables as input. The results of regression model indicate that size, legal status, outreach and service provisions significantly affect SPI. ANN analysis result indicates that social performance of MFIs gets determined by MFI specific internal factors. The experimental result indicates that the proposed ANN prediction model is providing better result for predicting the SPI. The findings suggest that MFIs can contribute for development of the society by adopting suitable policies keeping in view certain internal factors.
Article Details
References
Abdulai, A. and Tewari, D. D. (2017). Trade-off between outreach and sustainability of microfinance institutions?: evidence from sub-Saharan Africa. Enterprise Development and Microfinance, 28(3), 162-181.
Barry, T. A., & Tacneng, R. (2014). The Impact of Governance and Institutional Quality on MFI Outreach and Financial Performance in Sub-Saharan Africa. World Development, 58, 1–20.
Condori-alejo, H. I., Aceituno-rojo, M. R., & Sotomayor, G. (2021). Rural Micro Credit Assessment using Machine Learning in a Peruvian microfinance institution. Procedia Computer Science, 187, 408–413.
Cull, R., Demirgüç-Kunt, A., & Morduch, J. (2009). Microfinance meets the market. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 23(1), 167–192.
Desa, G., & Koch, J. L. (2014). Scaling Social Impact: Building Sustainable Social Ventures at the Base-of-the-Pyramid. Journal of Social Entrepreneurship, 5(2), 146–174.
D'Espallier, B., Hudon, M. and Szafarz, A. (2013). Unsubsidized microfinance institutions. Economics Letters, 120(2), 174–176.
Engels, P. (2009). Mission Drift in Microfinance , the influence of institutional and country risk indicators on the trade-off between the financial and social performance of microfinance institutions. https://www.socioeco.org/bdf_fiche-document-6404_en.html
Espallier, B. D., Hudon, M., & Szafarz, A. (2013). Unsubsidized microfinance institutions. Economics Letters, 120(2), 174–176.
Gutiérrez-Nieto, B., Serrano-Cinca, C., & Mar Molinero, C. (2009). Social efficiency in microfinance institutions. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 60(1), 104–119.
Hajji, T. and Jamil, O. M. (2019). Rating Microfinance Products Consumers Using Artificial Neural Networks. In: Rocha, Á. Serrhini, M. (eds) Information Systems and Technologies to Support Learning. EMENA-ISTL 2018. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, 111, 460–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03577-8_51
Hermes, N., & Lensink, Robert and MEESTERS, A. (2011). Outreach and Efficiency of Microfinance Institutions. World Development, 39(6), 938–948.
Kar, A. K. (2013). Mission drift in microfinance: Are the concerns really worrying? Recent cross-country results. International Review of Applied Economics, 27(1), 44–60.
Kogut, B. (1985). Designing Global Strategies: Comparative and Competitive Value-Added Chains. Sloan Management Review, 26(4), 15–28.
Lyon, F., & Fernandez, H. (2012). Strategies for scaling up social enterprise: lessons from early years providers. Social Enterprise Journal, 8(1), 63–77.
Marr, Ana, & Awaworyi, Sefa (2012). Microfinance social performance?: A global empirical study. Applied Econometrics and International Development, 12 (2), 51-68.
Mersland, R., & Øystein Strøm, R. (2009). Performance and governance in microfinance institutions. Journal of Banking and Finance, 33(4), 662–669.
Mersland, R., & Strøm, R. Ø. (2010). Microfinance Mission Drift? World Development, 38(1), 28–36.
Mia, A. &, Chandran, & V.G.R. (2016). Measuring Financial and Social Outreach Productivity of Microfinance Institutions in Bangladesh. Social Indicators Research, 127(2), 505–527.
Mohanty, B. K. and Samanta, S. (2022). Measuring the Impact of Electrification on Socio-Economic Development of Rural Odisha. Water and Energy International, 65(4), 52-57.
Morduch, J. (1999). The microfinance promise. Journal of Economic Literature, 37(4), 1569–1614.
Nanda, A.K. and Samanta, S. (2018). Mainstreaming tribals through financial literacy – a review of literature. International Journal of Social Economics, 45(2), 437-444.
Narwal, K. P., & Yadav, M. K. (2014). Impact of Characteristics on Outreach and Profitability of Microfinance Institution in India. International Journal of Financial Management, 4(3), 50-57.
Navajas et al. (2000). Microcredit and the poorest of the poor: Theory and evidence from Bolivia. World Development, 28(2), 333–346.
Paxton, J. (2007). Technical Efficiency in a Semi-Formal Financial Sector?: The Case of Mexico. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics, 69(1), 57–74.
Rashid, Abdul and Twaha, K. (2013). Exploring the determinants of the productivity of indian microfinance institutions. Theoretical and Applied Economics, XX(12), 83–96.
Rup, B.K., Gochhayat, J. and Samanta, S. (2018). Influence of Social Construct on Consumers’ Brand Purchase Intention: a Review of Research. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 7(3), 511-515.
Samanta, S. and Nanda, A. K. (2019). Financial Literacy Lead to Empowering the Socio-Economic Condition of Tribals through Information Technology. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology,10(1), 327-341.
Snigdha, S., Sasmita, S. and Arpita, M. (2020). Economic victimisation of convict’s family: Statistical analysis through SPSS. International Journal of Knowledge-based and Intelligent Engineering Systems, 24(3), 261-268.
Tchakoute-tchuigoua, H. (2010). Is there a difference in performance by the legal status of microfinance institutions?? Quarterly Review of Economics and Finance, 50(4), 436–442.
Uvin, P. (1995). Fighting hunger at the grassroots: Paths to scaling up. World Development, 23(6), 927–939.
Wijesiri, M., Viganò, L., & Meoli, M. (2015a). Ef fi ciency of micro fi nance institutions in Sri Lanka?: a two-stage double bootstrap DEA approach. Economic Modelling, 47, 74–83.
Yaroshchuk, S. O., Shapovalova, N. N., Striuk, A. M., Rybalchenko, O. H., Dotsenko, I. O., & Bilashenko, S. V. (2019). Credit scoring model for microfinance organizations. 115–127. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2546/paper07.pdf
Zhong, X., & Zhou, S. (2020). Risk analysis method of bank microfinance based on multiple genetic artificial neural networks. Neural Computing and Applications, 32, 5367–5377.