Exploring Post-Adoption Behavior of the UPI users with Cognitive and Affective Factors
Main Article Content
Abstract
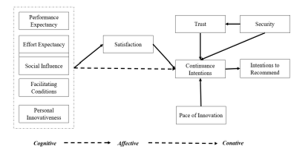
The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has invested a sizable amount of money in the country's massive payment infrastructure in an effort to enhance the user experience. However, in order for investments to be profitable, NPCI must guarantee the ongoing use of technological solutions and post-adoptive behaviors like continuance and recommendation intention. The impact of cognitive factors (i.e. Performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influences, facilitating conditions; personal innovativeness) and affective factors (such as satisfaction) on conative factors (such as continuation and recommendation intention) in the perspective of UPI applications (apps) was investigated using the UTAUT model. Partial Least Square Structural Equation Modeling when applied on 651 users (PLS-SEM) showed that satisfaction had a direct impact on continuation intentions, which in turn had an impact on recommendations intentions. It was discovered that all cognitive factors, including performance expectations, effort expectations, and facilitating conditions, have an impact on satisfaction. According to the study, adding a significant individual difference variable—personal innovativeness with regard to information technology—would aid in our understanding of the role that these factors play in the development of continuous intention. It further examines the influence of trust and security, and the pace of innovation on continued intentions. Through the mediating function of user satisfaction, it also looked at the impact of performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, facilitating variable, and personal innovativeness on the continuance intentions of the UPI system. All factors have been shown to be significant. Future researchers will find it extremely helpful that the study used a validated instrument to better understand user adherence and referral intentions. Therefore, this study adds to the limited body of knowledge in the payment industry literature by examining how users perceive UPI apps and post-adoption behaviors.
Article Details
References
Agarwal, R., & Dhar, V. (2014). Editorial —Big Data, Data Science, and Analytics: The Opportunity and Challenge for IS Research. Information Systems Research, 25(3), 443–448. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.2014.0546
Agrebi S, Jallais J. Explain the intention to use smartphones for mobile shopping. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. 2015;22:16-23. doi:10.1016/j.jretconser.2014.09.003
Al-Maroof S Rana, Alhumaid K, Salloum S. The Continuous Intention to Use E-Learning, from Two Different Perspectives. Education Sciences. 2020;11(1):6. doi:10.3390/educsci11010006
Arfi WB, Nasr IB, Kondrateva G, Hikkerova L. The role of trust in intention to use the IoT in eHealth: Application of the modified UTAUT in a consumer context. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. 2021;167:120688. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120688.
Arkorful, V., &Abaidoo, N. (2015). The role of e-learning, advantages and disadvantages of its adoption in higher education. International journal of instructional technology and distance learning, 12(1), 29-42.
Bhattacherjee A. Understanding Information Systems Continuance: An Expectation-Confirmation Model. MIS Quarterly. 2001;25(3):351. doi:10.2307/3250921
Byrne, D., Oliner, S. D., &Sichel, D. E. (2017). Prices of high-tech products, mismeasurement, and the pace of innovation. Business Economics, 52(2), 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1057/s11369-017-0034-4
Camilleri MA. Measuring the hoteliers’ interactive engagement through social media. In14th European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship (ECIE2019), University of Peloponnese, Kalamata, Greece 2019 Sep 19.
Camilleri, M. A., & Camilleri, A. C. (2017). Digital learning resources and ubiquitous technologies in education. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 22(1), 65-82.
Cao X, Yu L, Liu Z, Gong M, Adeel L. Understanding mobile payment users’ continuance intention: a trust transfer perspective. Internet Research. 2018;28(2):456-476. doi:10.1108/IntR-11-2016-0359
Chao CM. Factors determining the behavioral intention to use mobile learning: An application and extension of the UTAUT model. Frontiers in psychology. 2019;10:1652.
Chen, S.-C., Yen, D. C., & Hwang, M. I. (2012). Factors influencing the continuance intention to the usage of Web 2.0: An empirical study. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(3), 933- 941
Choi, M., Han, K., & Choi, J. (2015). The effects of product attributes and service quality of transportation card solutions on service user’s continuance and word-of-mouth intention. Service Business, 9(3), 463–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-014-0235-0
Chong AYL. Predicting m-commerce adoption determinants: A neural network approach. Expert Systems with Applications. 2013;40(2):523-530. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2012.07.068
Deng, Z., Lu, Y., Wei, K. K., & Zhang, J. (2010). Understanding customer satisfaction and loyalty: An empirical study of mobile instant messages in China. International journal of information management, 30(4), 289-300.
Dixit, S., Maurya, M., Sharma, N., & Zaidi, N. (2022). Payments Process Privilege: Leveraging Fintech with TAM. 2022 8th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), 1668–1673. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCS54159.2022.9785136
Engeström, Y. (1987). An activity-theoretical approach to developmental research. Learning by Expanding.
F. Hair Jr, J., Sarstedt, M., Hopkins, L., & G. Kuppelwieser, V. (2014). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): An emerging tool in business research. European Business Review, 26(2), 106–121. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-10-2013-0128
Faaeq MK, Alqasa K, Al-Matari EM. Technology adoption and innovation of E-Government in Republic of Iraq. Asian Social Science. 2014;11(3):135-45.
Fornell C, Larcker DF. Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics. Journal of Marketing Research. 1981;18(3):382-388. doi:10.1177/002224378101800313.
Fouillet C, Guérin I, Servet JM. Demonetization and digitalization: The Indian government’s hidden agenda. Telecommunications Policy. 2021;45(2):102079. doi:10.1016/j.telpol.2020.102079
Gao L, Waechter KA, Bai X. Understanding consumers’ continuance intention towards mobile purchase: A theoretical framework and empirical study – A case of China. Computers in Human Behavior. 2015; 53:249-262. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.014
Gholami R, Ogun A, Koh E, Lim J. Factors affecting e-payment adoption in Nigeria. Journal of Electronic Commerce in Organizations (JECO). 2010;8(4):51-67.
Godambe AC. Unified Payments Interface (UPI)- Advantages and Challenges. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology. 2020; 7(12): 971-973
Goldsmith RE, Hofacker CF. Measuring consumer innovativeness. Journal of the academy of marketing science. 1991 Jun;19(3):209-21.
Hair JF, Hult GTM, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M, Danks NP, Ray S. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook. Springer International Publishing; 2021. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-80519-7.
Han DI, tom Dieck MC, Jung T. User experience model for augmented reality applications in urban heritage tourism. Journal of Heritage Tourism. 2018;13(1):46-61.
Hsiao CH, Chang JJ, Tang KY. Exploring the influential factors in continuance usage of mobile social Apps: Satisfaction, habit, and customer value perspectives. Telematics and Informatics. 2016;33(2):342-55.
Hung, M. C., Yang, S. T., & Hsieh, T. C. (2012). An examination of the determinants of mobile shopping continuance. International Journal of Electronic Business Management, 10(1), 29.
Kamboj S, Joshi R. Examining the factors influencing smartphone apps use at tourism destinations: a UTAUT model perspective. IJTC. 2021;7(1):135-157. doi:10.1108/IJTC-05-2020-0094.
Khanra, S., Joseph, R. P., Dhir, A., & Kaur, P. (2020). Antecedents of the Barriers Toward the Adoption of Unified Payment Interface. In S. K. Sharma, Y. K. Dwivedi, B. Metri, & N. P. Rana (Eds.), Re-imagining Diffusion and Adoption of Information Technology and Systems: A Continuing Conversation (Vol. 618, pp. 608–625). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64861-9_53
Kim DJ, Kim GJ (2010) A comparative study between product and service for process to form intent of repeat-visit and word-of-mouth: case of family restaurants in Daegu region. Korean J Hotel Adm 19(3):131–146
Kim J, Lee KS. Conceptual model to predict Filipino teachers’ adoption of ICT-based instruction in class: using the UTAUT model. Asia Pacific Journal of Education. 2020 Jun 20:1-5.
Kim MJ, Chung N, Lee CK, Preis MW. Motivations and Use Context in Mobile Tourism Shopping: Applying Contingency and Task-Technology Fit Theories: Motivations and Use Context in Mobile Tourism Shopping. International Journal of Tourism Research. 2015;17(1):13-24. doi:10.1002/jtr.1957
Kim S, Bae J, Jeon H. Continuous Intention on Accommodation Apps: Integrated Value-Based Adoption and Expectation–Confirmation Model Analysis. Sustainability. 2019;11(6):1578. doi:10.3390/su11061578.
Kim, Y. H., Kim, D. J., & Wachter, K. (2013). A study of mobile user engagement (MoEN): Engagement motivations, perceived value, satisfaction, and continued engagement intention. Decision Support Systems, 56, 361–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2013.07.002
Kumar A, Upadhyay P, Sharma SK, Gupta P. Role of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors Affecting Continuance Intentions of Digital Payment Services. In: Sharma SK, Dwivedi YK, Metri B, Rana NP, eds. Re-Imagining Diffusion and Adoption of Information Technology and Systems: A Continuing Conversation. Vol 618. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology. Springer International Publishing; 2020:544-555. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-64861-9_48
Kuo YF, Wu CM, Deng WJ. The relationships among service quality, perceived value, customer satisfaction, and post-purchase intention in mobile value-added services. Computers in human behavior. 2009;25(4):887-96.
Leavitt C, Walton J. Development of a scale for innovativeness. ACR North American Advances. 1975.
Lee CY, Tsao CH, Chang WC. The relationship between attitude toward using and customer satisfaction with mobile application services: An empirical study from the life insurance industry. Journal of Enterprise Information Management. 2015;28(5):680-697. doi:10.1108/JEIM-07-2014-0077
Li H, Liu J, Zhang D, Liu H. Examining the relationships between cognitive activation, self?efficacy, socioeconomic status, and achievement in mathematics: A multi?level analysis. British Journal of Educational Psychology. 2021;91(1):101-26.
Li W, Xue L. Analyzing the Critical Factors Influencing Post-Use Trust and Its Impact on Citizens’ Continuous-Use Intention of E-Government: Evidence from Chinese Municipalities. Sustainability. 2021;13(14):7698. doi:10.3390/su13147698.
Liang TP, Lai CY, Hsu PH, Chiu CM, Hsieh CT. Factors affecting satisfaction and brand loyalty to smartphone systems: a perceived benefits perspective. IJMC. 2018;16(5):513. doi:10.1504/IJMC.2018.094353
Liébana-Cabanillas F, Marinkovi? V, Kalini? Z. A SEM-neural network approach for predicting antecedents of m-commerce acceptance. International Journal of Information Management. 2017;37(2):14-24.
Llewellyn, R. S., & Brown, B. (2020). Predicting adoption of innovations by farmers: What is different in smallholder agriculture?. Applied Economic Perspectives and Policy, 42(1), 100-112.
Lu J. Are personal innovativeness and social influence critical to continue with mobile commerce? Internet Research. 2014;24(2):134-159. doi:10.1108/IntR-05-2012-0100
Madwanna, Y., Khadse, M., &Chandavarkar, B. R. (2021). Security Issues of Unified Payments Interface and Challenges: Case Study. 2021 2nd International Conference on Secure Cyber Computing and Communications (ICSCCC), 150–154. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSCCC51823.2021.9478078
Mani, S., & Dhingra, T. (2012). Diffusion of innovation model of consumer behaviour – Ideas to accelerate adoption of renewable energy sources by consumer communities in India. Renewable Energy, 39(1), 162–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2011.07.036
Marinkovi? V, ?or?evi? A, Kalini? Z. The moderating effects of gender on customer satisfaction and continuance intention in mobile commerce: a UTAUT-based perspective. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management. 2020;32(3):306-318. doi:10.1080/09537325.2019.1655537
Marinkovi? V, ?or?evi? A, Kalini? Z. The moderating effects of gender on customer satisfaction and continuance intention in mobile commerce: a UTAUT-based perspective. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management. 2020;32(3):306-18.
Mishra, KD. A Review on Unified Payment Interface [UPI]. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology. 2017;4(6): 5620-5623
Mubarokah, I., &Hidayanto, A. N. (2020, November).Analysis of Continuance Use Intention and Satisfaction on Implementation of ALKI (Internal Activity Report Application) in Ministry of Industry. In 2020 International Conference on Informatics, Multimedia, Cyber and Information System (ICIMCIS) (pp. 307-312).IEEE.
Nielsen, P., & Sahay, S. (2022). A critical review of the role of technology and context in digital health research. DIGITAL HEALTH, 8, 205520762211095. https://doi.org/10.1177/20552076221109554
Olatubosun O, Madhava Rao KS. Empirical study of the readiness of public servants on the adoption of e-government. International Journal of Information Systems and Change Management. 2012;6(1):17-37.
Pappas, I. O., Kourouthanassis, P. E., Giannakos, M. N., &Chrissikopoulos, V. (2016). Explaining online shopping behavior with fsQCA: The role of cognitive and affective perceptions. Journal of Business Research, 69(2), 794–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.07.010
Park, K., &Koh, J. (2017). Exploring the relationship between perceived pace of technology change and adoption resistance to convergence products. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 142-150.
Perkins, D. N., Jay, E., & Tishman, S. (1993). Beyond Abilities: A Dispositional Theory of Thinking. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 39(1), 1–21. http://www.jstor.org/stable/23087298
Plotzky C, Lindwedel U, Sorber M, et al. Virtual reality simulations in nurse education: A systematic mapping review. Nurse Education Today. 2021;101:104868. doi:10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104868.
Prensky, M. (2005). Computer games and learning: Digital game-based learning. Handbook of computer game studies, 18, 97-122
Putra RL, Setiawan M, Hussein AS, Yuniarinto A. Perceived Digital Value Toward Continuous Intention to Use Among Mobile Payment Users During Pandemic Outbreak. Frontiers in Psychology. 2022;13.
PwC (2021), Report, The Indian payments handbook – 2021–2026.
Rai, A., Lang, S. S., & Welker, R. B. (2002). Assessing the validity of IS success models: An empirical test and theoretical analysis. Information systems research, 13(1), 50-69
Rezaei, S., &Valaei, N. (2017). Branding in a multichannel retail environment: Online stores vs app stores and the effect of product type. Information Technology & People, 30(4), 853–886. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-12-2015-0308
Safeena R, Kammani A, Date H. Exploratory Study of Internet Banking Technology Adoption: International Journal of E-Services and Mobile Applications. 2017;9(2):23-43. doi:10.4018/IJESMA.2017040102
Salim, T. A., El Barachi, M., Onyia, O. P., & Mathew, S. S. (2020). Effects of smart city service channel-and user-characteristics on user satisfaction and continuance intention. Information Technology & People
Sandeep kaur and Rupinder Katoch. Factors Influencing Continuance Intentions of Unified Payment Interface (UPI) users, 19 August 2022, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square [https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1966920/v1]
San-Martin S, Jimenez N, Liebana-Cabanillas F. Tourism value VS barriers to booking trips online. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. 2020;53:101957.
Saparudin M, Rahayu A, Hurriyati R, Sultan MokhA, Ramdan AM. Consumers’ Continuance Intention Use of Mobile Banking in Jakarta: Extending UTAUT Models with Trust. In: 2020 International Conference on Information Management and
Sarabadani J, Jafarzadeh H, ShamiZanjani M. Towards Understanding the Determinants of Employees' E-Learning Adoption in Workplace: A Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) View. International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems (IJEIS). 2017;13(1):38-49.
Saxena S. Role of “perceived risks” in adopting mobile government (m-government) services in India. Foresight. 2018;20(2):190-205. doi:10.1108/FS-08-2017-0040.
Setiani N, Aditya BR, Wijayanto I, Wijaya A. Acceptance and Usage of Bibliographic Management Software in Higher Education: The Student and Teacher Point of View. In: 2020 IEEE Conference on E-Learning, e-Management and e-Services (IC3e). IEEE; 2020:55-60. doi:10.1109/IC3e50159.2020.9288437
Shaikh, A. A., & Karjaluoto, H. (2015). Mobile banking adoption: A literature review. Telematics and informatics, 32(1), 129-142.
Shang D, Wu W. Understanding mobile shopping consumers’ continuance intention. IMDS. 2017;117(1):213-227. doi:10.1108/IMDS-02-2016-0052
Shao Yeh Y, Li Y. Building trust in m?commerce: contributions from quality and satisfaction. Online Information Review. 2009;33(6):1066-1086. doi:10.1108/14684520911011016.
Shao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Guo, Y. Antecedents of Trust and Continuance Intention in Mobile Payment Plat-forms: The Moderating Effect of Gender. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2018, 33, 100823. [CrossRef]
Shehryar, O., & Hunt, D. M. (2005). Buyer behavior and procedural fairness in pricing: Exploring the moderating role of product familiarity. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 14(4), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1108/10610420510609294
Sreejesh S, Sarkar JG, Sarkar A. Digital healthcare retail: role of presence in creating patients’ experience. IJRDM. 2022;50(1):36-54. doi:10.1108/IJRDM-12-2020-0514.
Susanto A, Chang Y, Ha Y. Determinants of continuance intention to use the smartphone banking services: An extension to the expectation-confirmation model. Industrial Management & Data Systems. 2016;116(3):508-25.
Tan GW, Ooi KB. Gender and age: Do they really moderate mobile tourism shopping behavior? Telematics and Informatics. 2018;35(6):1617-42.
Technology (ICIMTech). IEEE; 2020:50-54. doi:10.1109/ICIMTech50083.2020.9211188
Turan A, Tunç AÖ, Zehir C. A theoretical model proposal: Personal innovativeness and user involvement as antecedents of unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2015;210:43-51.
Upadhyay, P., Kumar, A., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Adlakha, A. (2022). Continual usage intention of platform-based governance services: A study from an emerging economy. Government Information Quarterly, 39(1), 101651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2021.101651
Usman O, Monoarfa T, Marsofiyati M. E-Banking and mobile banking effects on customer satisfaction. Accounting. 2020;6(6):1117-28.
Venkatesh V, Morris MG, Davis GB, Davis FD. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS quarterly. 2003:425-78.
Wan L, Xie S, Shu A. Toward an understanding of university students’ continued intention to use MOOCs: When UTAUT model meets TTF model. Sage Open. 2020;10(3):2158244020941858.
Wan, L., Xie, S., & Shu, A. (2020). Toward an understanding of university students’ continued intention to use MOOCs: When UTAUT model meets TTF model. Sage Open, 10(3), 2158244020941858.
Wang, W. T., Ou, W. M., & Chen, W. Y. (2019). The impact of inertia and user satisfaction on the continuance intentions to use mobile communication applications: A mobile service quality perspective. International Journal of Information Management, 44, 178-193.
Wilkie, W. L. (1994). Consumer behavior. Wiley.
Wong CH, Tan GW, Tan BI, Ooi KB. Mobile advertising: the changing landscape of the advertising industry. Telematics and Informatics. 2015;32(4):720-34.
Zhang, P. (2013). The Affective Response Model: A Theoretical Framework of Affective Concepts and Their Relationships in the ICT Context. MIS Quarterly, 37(1), 247–274. https://doi.org/10.25300/MISQ/2013/37.1.11
Zhou T, Lu Y, Wang B. Integrating TTF and UTAUT to explain mobile banking user adoption. Computers in Human Behavior. 2010;26(4):760-767. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2010.01.013.