SarNet-1 -A Novel Architecture for Diagnosing Covid-19 Pneumonia and Pneumonia through Chest X-Ray Images
Main Article Content
Abstract
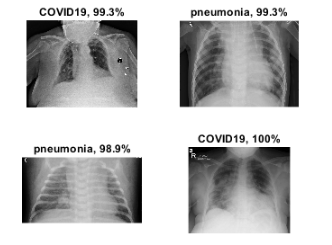
Coronavirus (COVID-19) is a contagious disease which begins with flu-like symptoms. COVID-19 arose in China and it rapidly spread throughout the globe, leading to a pandemic. For many, it was noticed that the infection started with fever, cough and finally leading to pneumonia. It is very necessary to differentiate between covid pneumonia and general pneumonia for appropriate treatment. Chest X-ray readings are useful for radiologists to identify the severity of infection. While computerising this mechanism, deep learning techniques are found to be very useful in extracting relevant features from medical images. This can help in differentiating pneumonia, COVID19 pneumonia and x-rays of a healthy person. Computer aided methods for identifying the presence of pneumonia can help health providers to a great extent for quick diagnosis. The X-ray’s gathered from freely available datasets are used in this work to propose an architecture for categorising X-ray’s into pneumonia and covid pneumonia.
Article Details
References
S. Albahli, “Efficient gan-based chest radiographs (CXR) augmentation to diagnose coronavirus disease pneumonia,” Int. J. Med. Sci., vol. 17, no. 10, pp. 1439–1448, 2020, doi: 10.7150/ijms.46684.
K. H. Shibly, S. K. Dey, M. T. U. Islam, and M. M. Rahman, “COVID faster R–CNN: A novel framework to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in X-Ray images,” Informatics Med. Unlocked, vol. 20, p. 100405, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2020.100405.
S. V Militante and B. G. Sibbaluca, “Pneumonia Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks,” [Online]. Available: www.ijstr.org.
P. Rajpurkar et al., “CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-Rays with Deep Learning,” Nov. 2017, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05225.
K. Hamano-Hasegawa et al., “Comprehensive detection of causative pathogens using real-time PCR to diagnose pediatric community-acquired pneumonia,” J. Infect. Chemother., vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 424–432, 2008, doi: 10.1007/s10156-008-0648-6.
K. El Asnaoui, Y. Chawki, and A. Idri, “Automated Methods for Detection and Classification Pneumonia based on X-Ray Images Using Deep Learning,” 2021.
J. Chastre and J.-Y. Fagon, “State of the Art Ventilator-associated Pneumonia,” Am J Respir Crit Care Med, vol. 165, pp. 867–903, 2002, doi: 10.1164/rccm.2105078.
M. F. Hashmi, S. Katiyar, A. G. Keskar, N. D. Bokde, and Z. W. Geem, “Efficient pneumonia detection in chest xray images using deep transfer learning,” Diagnostics, vol. 10, no. 6, Jun. 2020, doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10060417.
N. K. Chowdhury, M. A. Kabir, M. M. Rahman, and N. Rezoana, “ECOVNet: An Ensemble of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based on EfficientNet to Detect COVID-19 From Chest X-rays,” Sep. 2020, doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.551.
J. C. Gomes et al., “IKONOS: An intelligent tool to support diagnosis of Covid-19 by texture analysis of x-ray images.”
D. Kollias, A. Tagaris, A. Stafylopatis, S. Kollias, and G. Tagaris, “Deep neural architectures for prediction in healthcare,” Complex Intell. Syst., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 119–131, Jun. 2018, doi: 10.1007/s40747-017-0064-6.
A. Narin, C. Kaya, and Z. Pamuk, “Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks,” Pattern Anal. Appl., vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 1207–1220, 2021, doi: 10.1007/s10044-021-00984-y.
M. E. H. Chowdhury et al., “Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia?,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 132665–132676, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3010287.
L. Alzubaidi et al., “Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions,” J. Big Data, vol. 8, no. 1, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8.
L. O. Hall, R. Paul, D. B. Goldgof, and G. M. Goldgof, “Finding COVID-19 from Chest X-rays using Deep Learning on a Small Dataset.” [Online]. Available: https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset.
P. K. Sethy, S. K. Behera, P. K. Ratha, and P. Biswas, “Detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) based on deep features and support vector machine,” Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci., vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 643–651, 2020, doi: 10.33889/IJMEMS.2020.5.4.052.
S. Albahli and G. N. A. Hassan Yar, “Fast and accurate detection of COVID-19 along with 14 other chest pathologies using a multi-level classification: Algorithm development and validation study,” J. Med. Internet Res., vol. 23, no. 2, Feb. 2021, doi: 10.2196/23693.
S. Hassantabar, M. Ahmadi, and A. Sharifi, “Diagnosis and detection of infected tissue of COVID-19 patients based on lung x-ray image using convolutional neural network approaches,” Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, vol. 140, p. 110170, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110170.
R. Karthik, R. Menaka, and M. Hariharan, “Learning distinctive filters for COVID-19 detection from chest X-ray using shuffled residual CNN,” no. January, 2020.
E. F. Ohata et al., “Automatic detection of COVID-19 infection using chest X-ray images through transfer learning,” IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 239–248, 2021, doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003393.
J. de Moura et al., “Deep convolutional approaches for the analysis of Covid-19 using chest X-ray images from portable devices,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 195594–195607, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3033762.
Y. Lecun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, “Deep learning,” Nature, vol. 521, no. 7553, pp. 436–444, 2015, doi: 10.1038/nature14539.
K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, “Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition,” Dec. 2015, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385.
A. Ajit, K. Acharya, and A. Samanta, “A Review of Convolutional Neural Networks,” Feb. 2020, doi: 10.1109/ic-ETITE47903.2020.049.
T. Liu, S. Fang, Y. Zhao, P. Wang, and J. Zhang, “Implementation of Training Convolutional Neural Networks.”
T. N. Sainath, A. R. Mohamed, B. Kingsbury, and B. Ramabhadran, “Deep convolutional neural networks for LVCSR,” ICASSP, IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. - Proc., pp. 8614–8618, 2013, doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6639347.
“Pneumonia dataset.” https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia.
“covid-19 pneumonia data.” https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-clinical-center-provides- one-largestpublicly-available-chest-x-ray-datasets-scientific-community%0A(National institute of health)%0A.