Design and Implementation of Intelligent Traffic-Management System for Smart Cities using Roaming Agent and Deep Neural Network (RAD2N)
Main Article Content
Abstract
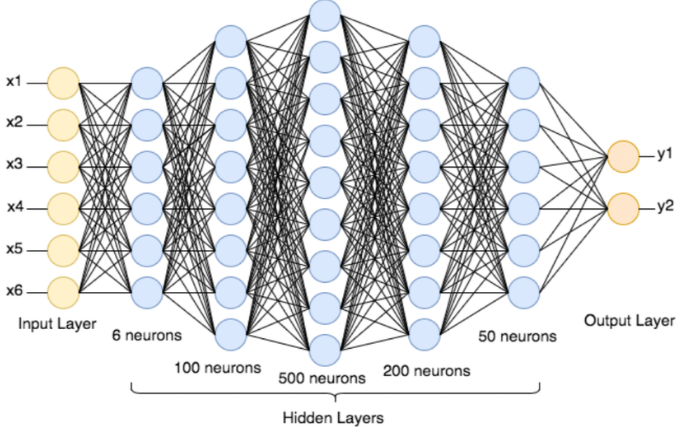
In metropolitan areas, the exponential growth in quantity of vehicles has instigated gridlock, pollution, and delays in the transportation of freight. IoT is the modern revolution which pushes the world towards intelligent management systems and automated procedures. This makes a significant contribution to automation and intelligent societies. Traffic regulation and effective congestion management assist conserve many priceless resources. In order to recognize, collect and send data, autonomous vehicles are furnished with IoT powered Intelligent Traffic Management System (ITMS) having a set of sensors. Moreover, machine learning (ML) algorithms can also be employed to enhance the transportation system. Traffic jams, delays, and a high death rate are the results of the problems that the current transport management systems face. In this paper, an active traffic control for VANET is proposed which merges Roaming Agents (RA) with deep neural networks (DNN). The effectiveness of the DNN with RA (RAD2N) routing method in VANETs is evaluated experimentally and compared with the traditional ML and other DL routing algorithms. Several traffic congestion indicators, including delay, packet delivery ratio (PDR) and throughput are used to validate RAD2N. The outcomes demonstrate that the proposed approach delivers lower latency and energy consumption.
Article Details
References
G. Blot, H. Fouchal, F. Rousseaux, and P. Saurel, “An experimentation ofVANETs for traffic management,” 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), 2016, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ICC.2016.7511127.
S. Li, Y. Liu, and J. Wang, “An efficient broadcast scheme for safety-related services in distributed TDMA-based VANETs,”IEEE Communications Letters, vol. 23, no. 8, pp. 1432-1436, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ICC.2016.7511127.
L. Shen, R. Liu, Z. Yao,W.Wu, and H. Yang, “Development of dynamic platoon dispersion models for predictive traffic signal control,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 431-440, Feb. 2019, doi:10.1109/TITS.2018.2815182.
Olayode, I.O.; Severino, A.; Campisi, T.; Tartibu, L.K. Prediction of Vehicular Traffic Flow using Levenberg-Marquardt Artificial Neural Network Model: Italy Road Transportation System. Commun.-Sci. Lett. Univ. Zilina 2021, 24, E74–E86. [CrossRef]
Bhatia, V.; Jaglan, V.; Kumawat, S.; Siwach, V.; Sehrawat, H. Intell?gent Transportat?on System Appl?cat?ons: A Traff?c Management Perspect?ve. In Intelligent Sustainable Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 419–433.
Manasseh, C.; Sengupta, R. Middleware to enhance mobile communications for road safety and traffic mobility applications. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2010, 4, 24–36. [CrossRef]
Zhang, Y.; Chu, L.; Fu, Z.; Xu, N.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.;Wang, P. Optimal energy management strategy for parallel plug-in hybrid electric vehicle based on driving behavior analysis and real time traffic information prediction. Mechatronics 2017, 46, 177–192. [CrossRef]
I. Ku, Y. Lu, M. Gerla, R. L. Gomes, F. Ongaro and E. Cerqueira, “Towards software-defined VANET: architecture and services,”2014 13th Annual Mediterranean Ad Hoc Networking Workshop (MED-HOC-NET),2014, pp.103-110, doi:10.1109/MedHocNet.2014.6849111.
R. Jia, P. Jiang, L. Liu, L. Cui, and Y. Shi, ``Data driven congestion trends prediction of urban transportation,'' IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 581_591, Apr. 2018.
F. Falahatraftar, S. Pierre, and S. Chamberland, ``A centralized and dynamic network congestion classi_cation approach for heterogeneous vehicular networks,'' IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 122284_122298, 2021.
Gatto, R.C.; Forster, C.H.Q. Audio-Based Machine Learning Model for Traffic Congestion Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 7200–7207. [CrossRef]
Tubaishat, M.; Zhuang, P.; Qi, Q.; Shang, Y. Wireless sensor networks in intelligent transportation systems. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2008, 9, 287–302. [CrossRef]
Padmaja, B.; Rao, P.V.N.; Bala, M.M.; Patro, E.K.R. A Novel Design of Autonomous Cars using IoT and Visual Features. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC)I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC), Palladam, India, 30–31 August 2018; pp. 18–21. [CrossRef]
K. Dass , A. ., & Lokhande , S. D. . (2023). Machine Learning Based Prediction of Obsolescence Risk . International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering, 11(4s), 293–301. Retrieved from https://ijisae.org/index.php/IJISAE/article/view/2667
Bhardwaj, K.K.; Khanna, A.; Sharma, D.K.; Chhabra, A. Designing energy-efficient IoT-based intelligent transport system: Need, architecture, characteristics, challenges, and applications. In Energy Conservation for IoT Devices; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 209–233.
Nosratabadi, S.; Mosavi, A.; Keivani, R.; Ardabili, S.; Aram, F. State of the Art Survey of Deep Learning and Machine Learning Models for Smart Cities and Urban Sustainability. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Global Research and Education, Balatonfüred, Hungary, 4–7 September 2019; pp. 228–238. [CrossRef]
Chen, C.; Xiang, H.; Qiu, T.;Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, V. A rear-end collision prediction scheme based on deep learning in the Internet of Vehicles. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2018, 117, 192–204. [CrossRef]
Balasubramaniam, A.; Paul, A.; Hong, W.-H.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.H. Comparative Analysis of Intelligent Transportation Systems for Sustainable Environment in Smart Cities. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1120. [CrossRef]
C. Song, H. Lee, C. Kang, W. Lee, Y. B. Kim, and S. W. Cha, “Traffic speed prediction under weekday using convolutional neuralnetworks concepts,” in 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), pp. 1293–1298, Los Angeles, CA, 2017.
D. Shengdong, T. Li, X. Gong, and S.-J. Horng, “A hybrid method for traffic flow forecasting using multimodal deep learning,” International journal of computational intelligence systems, vol. 13, pp. 85–97, 2020.
A. Hébert, T. Guédon, T. Glatard, and B. Jaumard, “High-resolution road vehicle collision prediction for the city of Montreal,” in 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), pp. 1804–1813, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2019.
Hussein,W.N.; Kamarudin, L.; Hussain, H.N.; Zakaria, A.; Ahmed, R.B.; Zahri, N. The Prospect of Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics in Transportation System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1018, 012013. [CrossRef]
Balasubramaniam, A.; Paul, A.; Hong, W.-H.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.H. Comparative Analysis of Intelligent Transportation Systems for Sustainable Environment in Smart Cities. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1120. [CrossRef]
Priyanka, E.B.; Thangavel, S.; Madhuvishal, V.; Tharun, S.; Raagul, K.V.; Krishnan, C.S.S. Application of Integrated IoT Framework to Water Pipeline Transportation System in Smart Cities. In Intelligence in Big Data Technologies—Beyond the Hype; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 571–579. [CrossRef]
Calabrese, M.; Cimmino, M.; Fiume, F.; Manfrin, M.; Romeo, L.; Ceccacci, S.; Paolanti, M.; Toscano, G.; Ciandrini, G.; Carrotta, A.; et al. SOPHIA: An Event-Based IoT and Machine Learning Architecture for Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0. Information 2020, 11, 202. [CrossRef]
Zear, A.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, Y. Intelligent Transport System: A Progressive Review. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 32. [CrossRef]
Wang, D.; Chen, D.; Song, B.; Guizani, N.; Yu, X.; Du, X. From IoT to 5G I-IoT: The Next Generation IoT-Based Intelligent Algorithms and 5G Technologies. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 114–120. [CrossRef]
Kiela, K.; Barzdenas, V.; Jurgo, M.; Macaitis, V.; Rafanavicius, J.; Vasjanov, A.; Kladovscikov, L.; Navickas, R. Review of V2X–IoT Standards and Frameworks for ITS Applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4314. [CrossRef]
P. Venkataram, S. Ghosal, and B. V. Kumar, “Neural network based optimal routing algorithm for communication networks,” Neural Networks, vol. 15, no. 10, pp. 1289–1298, 2002, doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(02)00067-9.
Patil, P. Smart IoT based system for vehicle noise and pollution monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICEI), Tirunelveli, India, 11–12 May 2017.
Zear, A.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, Y. Intelligent Transport System: A Progressive Review. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 32. [CrossRef]
Cheng, J.C.; Chen, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, Q. Data-driven predictive maintenance planning framework for MEP components based on BIM and IoT using machine learning algorithms. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103087. [CrossRef]
Jan, F.; Min-Allah, N.; Dü¸stegör, D. IoT based smart water quality monitoring: Recent techniques, trends, and challenges for domestic applications. Water 2021, 13, 1729. [CrossRef]
29. Asha, P.; Natrayan, L.; Geetha, B.; Beulah, J.R.; Sumathy, R.; Varalakshmi, G.; Neelakandan, S. IoT enabled environmental toxicology for air pollution monitoring using AI techniques. Environ. Res. 2021, 205, 112574. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Nocera, S.; Cavallaro, F. A Two-Step Method to Evaluate theWell-To-Wheel Carbon Efficiency of Urban Consolidation Centres. Res. Transp. Econ. 2017, 65, 44–55. [CrossRef]
John, S.K.; Sivaraj, D.; Mugelan, R.K. Implementation Challenges and Opportunities of Smart City and Intelligent Transport Systems in India. In Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics for Smart Generation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 213–235. [CrossRef]
Menouar, H.; Guvenc, I.; Akkaya, K.; Uluagac, A.S.; Kadri, A.; Tuncer, A. UAV-Enabled Intelligent Transportation Systems for the Smart City: Applications and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 22–28. [CrossRef]
Velaga, N.R.; Quddus, M.; Bristow, A. Developing an enhanced weight-based topological map-matching algorithm for intelligent transport systems. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2009, 17, 672–683. [CrossRef]
Martin, S., Wood, T., Hernandez, M., González, F., & Rodríguez, D. Machine Learning for Personalized Advertising and Recommendation. Kuwait Journal of Machine Learning, 1(4). Retrieved from http://kuwaitjournals.com/index.php/kjml/article/view/156
Mitsakis, E.; Kotsi, A. Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems as a Policy Tool for Mitigating the Impacts of Climate Change on Road Transport. In Data Analytics: Paving the Way to Sustainable Urban Mobility; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 418–425. [CrossRef]
Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, P.C.Y.; Liu, J. LSTM network: A deep learning approach for short-term traffic forecast. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 11, 68–75. [CrossRef]
Bugeja, M.; Dingli, A.; Attard, M.; Seychell, D. Comparison of Vehicle Detection Techniques applied to IP Camera Video Feeds for use in Intelligent Transport Systems. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 45, 971–978. [CrossRef]
Balasubramaniam, A.; Paul, A.; Hong, W.-H.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.H. Comparative Analysis of Intelligent Transportation Systems for Sustainable Environment in Smart Cities. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1120